A new element within the T-cell receptor alpha locus required for tissue-specific locus control region activity
- PMID: 10022877
- PMCID: PMC83983
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1901
A new element within the T-cell receptor alpha locus required for tissue-specific locus control region activity
Abstract
Locus control regions (LCRs) are cis-acting regulatory elements thought to provide a tissue-specific open chromatin domain for genes to which they are linked. The gene for T-cell receptor alpha chain (TCRalpha) is exclusively expressed in T cells, and the chromatin at its locus displays differentially open configurations in expressing and nonexpressing tissues. Mouse TCRalpha exists in a complex locus containing three differentially regulated genes. We previously described an LCR in this locus that confers T-lineage-specific expression upon linked transgenes. The 3' portion of this LCR contains an unrestricted chromatin opening activity while the 5' portion contains elements restricting this activity to T cells. This tissue-specificity region contains four known DNase I hypersensitive sites, two located near transcriptional silencers, one at the TCRalpha enhancer, and another located 3' of the enhancer in a 1-kb region of unknown function. Analysis of this region using transgenic mice reveals that the silencer regions contribute negligibly to LCR activity. While the enhancer is required for complete LCR function, its removal has surprisingly little effect on chromatin structure or expression outside the thymus. Rather, the region 3' of the enhancer appears responsible for the tissue-differential chromatin configurations observed at the TCRalpha locus. This region, herein termed the "HS1' element," also increases lymphoid transgene expression while suppressing ectopic transgene activity. Thus, this previously undescribed element is an integral part of the TCRalphaLCR, which influences tissue-specific chromatin structure and gene expression.
Figures

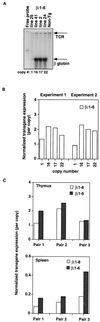
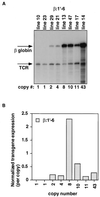
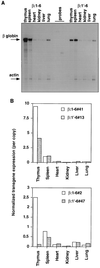
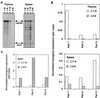

Similar articles
-
Adjacent DNA elements dominantly restrict the ubiquitous activity of a novel chromatin-opening region to specific tissues.EMBO J. 1997 Aug 15;16(16):5037-45. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.16.5037. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9305645 Free PMC article.
-
Control of organ-specific demethylation by an element of the T-cell receptor-alpha locus control region.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jan 21;275(3):1952-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1952. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10636897
-
Function and factor interactions of a locus control region element in the mouse T cell receptor-alpha/Dad1 gene locus.J Immunol. 2001 Oct 1;167(7):3836-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.7.3836. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11564801
-
Locus control regions.Blood. 2002 Nov 1;100(9):3077-86. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1104. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12384402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locus control regions: coming of age at a decade plus.Trends Genet. 1999 Oct;15(10):403-8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(99)01780-1. Trends Genet. 1999. PMID: 10498936 Review.
Cited by
-
Ectopic T cell receptor-α locus control region activity in B cells is suppressed by direct linkage to two flanking genes at once.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 22;5(11):e15527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015527. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124935 Free PMC article.
-
The 3'-Jα Region of the TCRα Locus Bears Gene Regulatory Activity in Thymic and Peripheral T Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132856. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177549 Free PMC article.
-
Adapting in vitro embryonic stem cell differentiation to the study of locus control regions.J Immunol Methods. 2014 May;407:135-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.03.012. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Immunol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24681242 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor α enhancer is inactivated in αβ T lymphocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 7;112(14):E1744-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406551112. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25831496 Free PMC article.
-
Complete TCR-α gene locus control region activity in T cells derived in vitro from embryonic stem cells.J Immunol. 2013 Jul 1;191(1):472-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300521. Epub 2013 May 29. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23720809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apte S S, Mattei M G, Seldin M F, Olsen B R. The highly conserved defender against the death 1 (DAD1) gene maps to human chromosome 14q11-q12 and mouse chromosome 14 and has plant and nematode homologues. FEBS Lett. 1995;323:304–306. - PubMed
-
- Aronow B J, Silbiger R N, Dusing M R, Stock J L, Yager K L, Potter S S, Hutton J J, Wiginton D A. Functional analysis of the human adenosine deaminase gene thymic regulatory region and its ability to generate position-independent transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:4170–4185. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagga R, Emerson B M. An HMG I/Y-containing repressor complex and supercoiled DNA topology are critical for long-range enhancer dependent transcription in vitro. Genes Dev. 1997;11:629–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
