Neu differentiation factor stimulates phosphorylation and activation of the Sp1 transcription factor
- PMID: 10022883
- PMCID: PMC83989
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1961
Neu differentiation factor stimulates phosphorylation and activation of the Sp1 transcription factor
Abstract
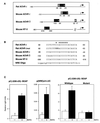
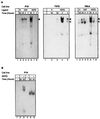
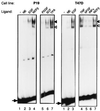
Neu differentiation factors (NDFs), or neuregulins, are epidermal growth factor-like growth factors which bind to two tyrosine kinase receptors, ErbB-3 and ErbB-4. The transcription of several genes is regulated by neuregulins, including genes encoding specific subunits of the acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction. Here, we have examined the promoter of the acetylcholine receptor epsilon subunit and delineated a minimal CA-rich sequence which mediates transcriptional activation by NDF (NDF-response element [NRE]). Using gel mobility shift analysis with an NRE oligonucleotide, we detected two complexes that are induced by treatment with neuregulin and other growth factors and identified Sp1, a constitutively expressed zinc finger phosphoprotein, as a component of one of these complexes. Phosphatase treatment, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, and an in-gel kinase assay indicated that Sp1 is phosphorylated by a 60-kDa kinase in response to NDF-induced signals. Moreover, Sp1 seems to act downstream of all members of the ErbB family and thus may funnel the signaling of the ErbB network into the nucleus.
Figures




References
-
- Alroy I, Yarden Y. The ErbB signaling network in embryogenesis and oncogenesis: signal diversification through combinatorial ligand-receptor interactions. FEBS Lett. 1997;410:83–86. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S A, Barry D A, Leggett R W, Mueller C R. Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of Sp1 decreases its DNA binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13489–13495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
