Activation-dependent transcriptional regulation of the human Fas promoter requires NF-kappaB p50-p65 recruitment
- PMID: 10022897
- PMCID: PMC84003
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.2098
Activation-dependent transcriptional regulation of the human Fas promoter requires NF-kappaB p50-p65 recruitment
Abstract
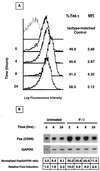
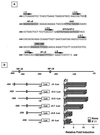
Fas (CD95) and Fas ligand (CD95L) are an interacting receptor-ligand pair required for immune homeostasis. Lymphocyte activation results in the upregulation of Fas expression and the acquisition of sensitivity to FasL-mediated apoptosis. Although Fas upregulation is central to the preservation of immunologic tolerance, little is known about the molecular machinery underlying this process. To investigate the events involved in activation-induced Fas upregulation, we have examined mRNA accumulation, fas promoter activity, and protein expression in the Jurkat T-cell line treated with phorbol myristate acetate and ionomycin (P/I), pharmacological mimics of T-cell receptor activation. Although resting Jurkat cells express Fas, Fas mRNA was induced approximately 10-fold in 2 h upon P/I stimulation. Using sequential deletion mutants of the human fas promoter in transient transfection assays, we identified a 47-bp sequence (positions -306 to -260 relative to the ATG) required for activation-driven fas upregulation. Sequence analysis revealed the presence of a previously unrecognized composite binding site for both the Sp1 and NF-kappaB transcription factors at positions -295 to -286. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and supershift analyses of this region documented constitutive binding of Sp1 in unactivated nuclear extracts and inducible binding of p50-p65 NF-kappaB heterodimers after P/I activation. Sp1 and NF-kappaB transcription factor binding was shown to be mutually exclusive by EMSA displacement studies with purified recombinant Sp1 and recombinant p50. The functional contribution of the kappaB-Sp1 composite site in P/I-inducible fas promoter activation was verified by using kappaB-Sp1 concatamers (-295 to -286) in a thymidine kinase promoter-driven reporter construct and native promoter constructs in Jurkat cells overexpressing IkappaB-alpha. Site-directed mutagenesis of the critical guanine nucleotides in the kappaB-Sp1 element documented the essential role of this site in activation-dependent fas promoter induction.
Figures
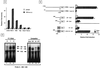

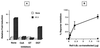

References
-
- Aries S, Scgaaf B, Muller C, Dennin R, Dalhoff K. Fas (CD95) expression of CD4+ T cells from HIV-infected patients increases with disease progression. J Mol Med. 1995;73:591–593. - PubMed
-
- Azizkhan J C, Jensen D E, Pierce A J, Wade M. Transcription from TATA-less promoters: dihydrofolate reductase as a model. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1993;3:229–254. - PubMed
-
- Behrmann I, Walczak H, Krammer P H. Structure of the human APO-1 gene. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:3057–3062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
