Reduced phosphorylation of p50 is responsible for diminished NF-kappaB binding to the major histocompatibility complex class I enhancer in adenovirus type 12-transformed cells
- PMID: 10022903
- PMCID: PMC84009
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.2169
Reduced phosphorylation of p50 is responsible for diminished NF-kappaB binding to the major histocompatibility complex class I enhancer in adenovirus type 12-transformed cells
Abstract
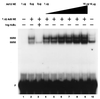
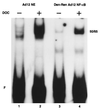
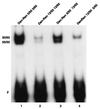
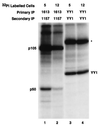
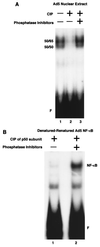
Reduced cell surface levels of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens enable adenovirus type 12 (Ad12)-transformed cells to escape immunosurveillance by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), contributing to their tumorigenic potential. In contrast, nontumorigenic Ad5-transformed cells harbor significant cell surface levels of class I antigens and are susceptible to CTL lysis. Ad12 E1A mediates down-regulation of class I transcription by increasing COUP-TF repressor binding and decreasing NF-kappaB activator binding to the class I enhancer. The mechanism underlying the decreased binding of nuclear NF-kappaB in Ad12-transformed cells was investigated. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay analysis of hybrid NF-kappaB dimers reconstituted from denatured and renatured p50 and p65 subunits from Ad12- and Ad5-transformed cell nuclear extracts demonstrated that p50, and not p65, is responsible for the decreased ability of NF-kappaB to bind to DNA in Ad12-transformed cells. Hypophosphorylation of p50 was found to correlate with restricted binding of NF-kappaB to DNA in Ad12-transformed cells. The importance of phosphorylation of p50 for NF-kappaB binding was further demonstrated by showing that an NF-kappaB dimer composed of p65 and alkaline phosphatase-treated p50 from Ad5-transformed cell nuclear extracts could not bind to DNA. These results suggest that phosphorylation of p50 is a key step in the nuclear regulation of NF-kappaB in adenovirus-transformed cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Tumorigenic adenovirus type 12 E1A inhibits phosphorylation of NF-kappaB by PKAc, causing loss of DNA binding and transactivation.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):40-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01579-07. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17959673 Free PMC article.
-
In adenovirus type 12 tumorigenic cells, major histocompatibility complex class I transcription shutoff is overcome by induction of NF-kappaB and relief of COUP-TFII repression.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3212-20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3212-3220.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884545 Free PMC article.
-
The first exon of Ad12 E1A excluding the transactivation domain mediates differential binding of COUP-TF and NF-kappa B to the MHC class I enhancer in transformed cells.Oncogene. 1996 Jan 4;12(1):143-51. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8552385
-
Evidence for the involvement of a nuclear NF-kappa B inhibitor in global down-regulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I enhancer in adenovirus type 12-transformed cells.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;16(1):398-404. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.1.398. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8524321 Free PMC article.
-
E1A-based determinants of oncogenicity in human adenovirus groups A and C.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;273:245-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-05599-1_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14674604 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumorigenic adenovirus 12 cells evade NK cell lysis by reducing the expression of NKG2D ligands.Immunol Lett. 2012 May 30;144(1-2):16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Immunol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22445355 Free PMC article.
-
The N terminus of adenovirus type 12 E1A inhibits major histocompatibility complex class I expression by preventing phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 Ser276 through direct binding.J Virol. 2010 Aug;84(15):7668-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02317-09. Epub 2010 May 26. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20504937 Free PMC article.
-
Tumorigenic adenovirus type 12 E1A inhibits phosphorylation of NF-kappaB by PKAc, causing loss of DNA binding and transactivation.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):40-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01579-07. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17959673 Free PMC article.
-
The MyoD-inducible p204 protein overcomes the inhibition of myoblast differentiation by Id proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(9):2893-905. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.9.2893-2905.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11940648 Free PMC article.
-
In adenovirus type 12 tumorigenic cells, major histocompatibility complex class I transcription shutoff is overcome by induction of NF-kappaB and relief of COUP-TFII repression.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3212-20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3212-3220.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackrill A M, Blair G E. Regulation of major histocompatibility class I gene expression at the level of transcription in highly oncogenic adenovirus transformed rat cells. Oncogene. 1988;3:483–487. - PubMed
-
- Ackrill A M, Blair G E. Nuclear proteins binding to an enhancer element of the major histocompatibility complex promoter: differences between highly oncogenic and nononcogenic adenovirus-transformed rat cells. Virology. 1989;172:643–646. - PubMed
-
- Andreu J M, de la Torre J, Carrascosa J L. Interaction of tubulin with octyl glucoside and deoxycholate. 2. Protein conformation, binding of colchicine ligands, and microtubule assembly. Biochemistry. 1986;25:5230–5239. - PubMed
-
- Andreu J M, Garcia de Ancos J, Starling D, Hodgkinson J L, Bordas J. A synchrotron X-ray scattering characterization of purified tubulin and of its expansion induced by mild detergent binding. Biochemistry. 1989;28:4036–4040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
