Mining SNPs from EST databases
Abstract
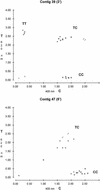
There is considerable interest in the discovery and characterization of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to enable the analysis of the potential relationships between human genotype and phenotype. Here we present a strategy that permits the rapid discovery of SNPs from publicly available expressed sequence tag (EST) databases. From a set of ESTs derived from 19 different cDNA libraries, we assembled 300,000 distinct sequences and identified 850 mismatches from contiguous EST data sets (candidate SNP sites), without de novo sequencing. Through a polymerase-mediated, single-base, primer extension technique, Genetic Bit Analysis (GBA), we confirmed the presence of a subset of these candidate SNP sites and have estimated the allele frequencies in three human populations with different ethnic origins. Altogether, our approach provides a basis for rapid and efficient regional and genome-wide SNP discovery using data assembled from sequences from different libraries of cDNAs.
Figures


References
-
- Adams MD, Soares MB, Kerlavage AR, Fields C, Venter JC. Rapid cDNA sequencing (expressed sequence tags) from a directionally cloned human infant brain cDNA library. Nat Genet. 1993;4:373–380. - PubMed
-
- Chee M, Yang R, Hubbell E, Berno A, Huang XC, Stern D, Winkler J, Lockhart DJ, Morris MS, Fodor SP. Accessing genetic information with high-density DNA arrays. Science. 1996;274:610–614. - PubMed
-
- Cl’ement K, Vaisse C, Lahlow N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambaz J, Lacorte JM, et al. A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature. 1998;392:398–401. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
