Identification of the Kv2.1 K+ channel as a major component of the delayed rectifier K+ current in rat hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 10024359
- PMCID: PMC6782166
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-05-01728.1999
Identification of the Kv2.1 K+ channel as a major component of the delayed rectifier K+ current in rat hippocampal neurons
Abstract
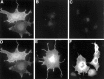
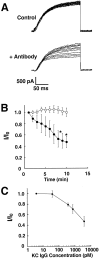
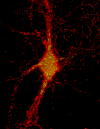
Molecular cloning studies have revealed the existence of a large family of voltage-gated K+ channel genes expressed in mammalian brain. This molecular diversity underlies the vast repertoire of neuronal K+ channels that regulate action potential conduction and neurotransmitter release and that are essential to the control of neuronal excitability. However, the specific contribution of individual K+ channel gene products to these neuronal K+ currents is poorly understood. We have shown previously, using an antibody, "KC, " specific for the Kv2.1 K+ channel alpha-subunit, the high-level expression of Kv2.1 protein in hippocampal neurons in situ and in culture. Here we show that KC is a potent blocker of K+ currents expressed in cells transfected with the Kv2.1 cDNA, but not of currents expressed in cells transfected with other highly related K+ channel alpha-subunit cDNAs. KC also blocks the majority of the slowly inactivating outward current in cultured hippocampal neurons, although antibodies to two other K+ channel alpha-subunits known to be expressed in these cells did not exhibit blocking effects. In all cases the blocking effects of KC were eliminated by previous incubation with a recombinant fusion protein containing the KC antigenic sequence. Together these studies show that Kv2.1, which is expressed at high levels in most mammalian central neurons, is a major contributor to the delayed rectifier K+ current in hippocampal neurons and that the KC antibody is a powerful tool for the elucidation of the role of the Kv2.1 K+ channel in regulating neuronal excitability.
Figures


References
-
- Archer SL, Souil E, Dinh-Xuan AT, Schremmer B, Mercier JC, El Yaagoubi A, Nguyen-Huu L, Reeve HL, Hampl V. Molecular identification of the role of voltage-gated K+ channels, Kv1.5 and Kv2.1, in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and control of resting membrane potential in rat pulmonary artery myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:2319–2330. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagetta G, Nistico G, Dolly JO. Production of seizures and brain damage in rats by α-dendrotoxin, a selective K+ channel blocker. Neurosci Lett. 1992;139:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Ballivet M, Nef B, Couturier S, Rungger D, Bader CR, Bertrand D, Cooper E. Electrophysiology of a chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes after cDNA injection. Neuron. 1988;1:847–852. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977;126:397–425. - PubMed
-
- Barry DM, Trimmer JS, Merlie JP, Nerbonne JM. Differential expression of voltage-gated K+ channel subunits in adult rat heart. Relation to functional K+ channels? Circ Res. 1995;77:361–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
