Alpha-toxin and gamma-toxin jointly promote Staphylococcus aureus virulence in murine septic arthritis
- PMID: 10024541
- PMCID: PMC96427
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.3.1045-1049.1999
Alpha-toxin and gamma-toxin jointly promote Staphylococcus aureus virulence in murine septic arthritis
Abstract
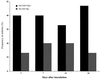
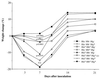
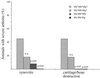
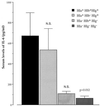
Septic arthritis is a common and feared complication of staphylococcal infections. Staphylococcus aureus produces a number of potential virulence factors including certain adhesins and enterotoxins. In this study we have assessed the roles of cytolytic toxins in the development of septic arthritis by inoculating mice with S. aureus wild-type strain 8325-4 or isogenic mutants differing in the expression of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-toxin production patterns. Mice inoculated with either an alpha- or beta-toxin mutant showed degrees of inflammation, joint damage, and weight decrease similar to wild-type-inoculated mice. In contrast, mice inoculated with either double (alpha- and gamma-toxin-deficient)- or triple (alpha-, beta-, and gamma-toxin-deficient)-mutant S. aureus strains showed lower frequency and severity of arthritis, measured both clinically and histologically, than mice inoculated with the wild-type strain. We conclude that simultaneous production of alpha- and gamma-toxin is a virulence factor in S. aureus arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Bauldry S A, Wooten R E, Bass D A. Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in permeabilized human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1299:223–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

