Referenceless interleaved echo-planar imaging
- PMID: 10025615
- PMCID: PMC2396321
- DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1522-2594(199901)41:1<87::aid-mrm13>3.0.co;2-x
Referenceless interleaved echo-planar imaging
Abstract
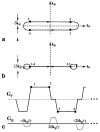
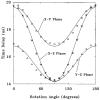
Interleaved echo-planar imaging (EPI) is an ultrafast imaging technique important for applications that require high time resolution or short total acquisition times. Unfortunately, EPI is prone to significant ghosting artifacts, resulting primarily from system time delays that cause data matrix misregistration. In this work, it is shown mathematically and experimentally that system time delays are orientation dependent, resulting from anisotropic physical gradient delays. This analysis characterizes the behavior of time delays in oblique coordinates, and a new ghosting artifact caused by anisotropic delays is described. "Compensation blips" are proposed for time delay correction. These blips are shown to remove the effects of anisotropic gradient delays, eliminating the need for repeated reference scans and postprocessing corrections. Examples of phantom and in vivo images are shown.
Figures







References
-
- Mansfield P. Multi-planar image formation using NMR spin-echoes. J Phys C. 1977;10:L55–L58.
-
- Kwong KK. Functional magnetic resonance imaging with echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Q. 1995;11:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Turner R, LeBihan D. Single-shot diffusion imaging at 2.0 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1990;86:445–452.
-
- Moseley ME, Sevick R, Wendland MF, White DL, Mintorovitch J, Asgari HS, Kucharczyk J. Ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging: diffusion and perfusion. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1991;42:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Stehling MK, Turner R, Mansfield P. Echo-planar imaging: magnetic resonance imaging in a fraction of a second. Science. 1991;254:43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

