Specific regional transcription of apolipoprotein E in human brain neurons
- PMID: 10027417
- PMCID: PMC1850012
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65305-9
Specific regional transcription of apolipoprotein E in human brain neurons
Abstract
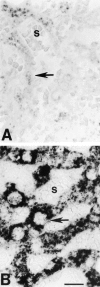
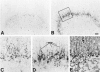
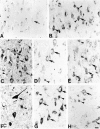
In central nervous system injury and disease, apolipoprotein E (APOE, gene; apoE, protein) might be involved in neuronal injury and death indirectly through extracellular effects and/or more directly through intracellular effects on neuronal metabolism. Although intracellular effects could clearly be mediated by neuronal uptake of extracellular apoE, recent experiments in injury models in normal rodents and in mice transgenic for the human APOE gene suggest the additional possibility of intraneuronal synthesis. To examine whether APOE might be synthesized by human neurons, we performed in situ hybridization on paraffin-embedded and frozen brain sections from three nondemented controls and five Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients using digoxigenin-labeled antisense and sense cRNA probes to human APOE. Using the antisense APOE probes, we found the expected strong hybridization signal in glial cells as well as a generally fainter signal in selected neurons in cerebral cortex and hippocampus. In hippocampus, many APOE mRNA-containing neurons were observed in sectors CA1 to CA4 and the granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus. In these regions, APOE mRNA containing neurons could be observed adjacent to nonhybridizing neurons of the same cell class. APOE mRNA transcription in neurons is regionally specific. In cerebellar cortex, APOE mRNA was seen only in Bergmann glial cells and scattered astrocytes but not in Purkinje cells or granule cell neurons. ApoE immunocytochemical localization in semi-adjacent sections supported the selectivity of APOE transcription. These results demonstrate the expected result that APOE mRNA is transcribed and expressed in glial cells in human brain. The important new finding is that APOE mRNA is also transcribed and expressed in many neurons in frontal cortex and human hippocampus but not in neurons of cerebellar cortex from the same brains. This regionally specific human APOE gene expression suggests that synthesis of apoE might play a role in regional vulnerability of neurons in AD. These results also provide a direct anatomical context for hypotheses proposing a role for apoE isoforms on neuronal cytoskeletal stability and metabolism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regionally specific neuronal expression of human APOE gene in transgenic mice.Neurosci Lett. 1998 Apr 24;246(2):65-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00247-x. Neurosci Lett. 1998. PMID: 9627181
-
Astroglial regulation of apolipoprotein E expression in neuronal cells. Implications for Alzheimer's disease.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 30;279(5):3862-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309475200. Epub 2003 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14585838
-
Neuron-specific apolipoprotein e4 proteolysis is associated with increased tau phosphorylation in brains of transgenic mice.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 10;24(10):2527-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4315-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15014128 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E as a target for developing new therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease based on studies from protein, RNA, and regulatory region of the gene.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(3):225-33. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:3:225. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15181251 Review.
-
ApoE and Aβ in Alzheimer's disease: accidental encounters or partners?Neuron. 2014 Feb 19;81(4):740-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.045. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24559670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Alzheimer-prone brain regions, metabolism and risk-gene expression are strongly correlated.Brain Commun. 2022 Aug 25;4(5):fcac216. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac216. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 36092303 Free PMC article.
-
Diet and age interactions with regards to cholesterol regulation and brain pathogenesis.Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2010;2010:219683. doi: 10.1155/2010/219683. Epub 2010 Apr 11. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20396385 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4: a causative factor and therapeutic target in neuropathology, including Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 11;103(15):5644-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600549103. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16567625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal ApoE4 in Alzheimer's disease and potential therapeutic targets.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jun 2;15:1199434. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1199434. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37333457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoE3 R136S binds to Tau and blocks its propagation, suppressing neurodegeneration in mice with Alzheimer's disease.Neuron. 2025 Mar 5;113(5):719-736.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.12.015. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Neuron. 2025. PMID: 39814008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahley RW: Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 1988, 240:622-630 - PubMed
-
- Weisgraber KH, Innerarity TL, Mahley RW: Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem 1982, 257:2518-2521 - PubMed
-
- Weisgraber KH: Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationship. Adv Protein Chem 1994, 45:249-302 - PubMed
-
- Pitas RE, Boyles JK, Lee SH, Foss D, Mahley RM: Astrocytes synthesize apolipoprotein E and metabolize apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Acta 1987, 917:148-161 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

