Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines
- PMID: 10029595
- PMCID: PMC5550098
Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines
Abstract
Integrin-mediated adhesion influences cell survival and may prevent programmed cell death. Little is known about how drug-sensitive tumor cell lines survive initial exposures to cytotoxic drugs and eventually select for drug-resistant populations. Factors that allow for cell survival following acute cytotoxic drug exposure may differ from drug resistance mechanisms selected for by chronic drug exposure. We show here that drug-sensitive 8226 human myeloma cells, demonstrated to express both VLA-4 (alpha4beta1) and VLA-5 (alpha5beta1) integrin fibronectin (FN) receptors, are relatively resistant to the apoptotic effects of doxorubicin and melphalan when pre-adhered to FN and compared with cells grown in suspension. This cell adhesion mediated drug resistance, or CAM-DR, was not due to reduced drug accumulation or upregulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members. As determined by flow cytometry, myeloma cell lines selected for drug resistance, with either doxorubicin or melphalan, overexpress VLA-4. Functional assays revealed a significant increase in alpha4-mediated cell adhesion in both drug-resistant variants compared with the drug-sensitive parent line. When removed from selection pressure, drug-resistant cell lines reverted to a drug sensitive and alpha4-low phenotype. Whether VLA-4-mediated FN adhesion offers a survival advantage over VLA-5-mediated adhesion remains to be determined. In conclusion, we have demonstrated that FN-mediated adhesion confers a survival advantage for myeloma cells acutely exposed to cytotoxic drugs by inhibiting drug-induced apoptosis. This finding may explain how some cells survive initial drug exposure and eventually express classical mechanisms of drug resistance such as MDR1 overexpression.
Figures



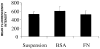


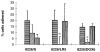
References
-
- Schustik C, Dalton WS, Gros P. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. Vol. 16. London, UK: Elsevier Science; 1995. P-glycoprotein–mediated multi-drug resistance in tumor cells: Biochemistry, clinical relevance and modulation; p. 1. - PubMed
-
- Dalton WS, Grogan TM, Rybski JA, Scheper RJ, Richter L, Kailey J, Broxterman HJ, Pinedo HM, Salmon SE. Immunohistochemical detection and quantification of P-glycoprotein in multiple drug-resistant human myeloma cells: Association with level of drug resistance and drug accumulation. Blood. 1989;73:747. - PubMed
-
- Durand RE, Sutherland RM. Effects of intercellular contact on repair of radiation damage. Exp Cell Res. 1972;71:75. - PubMed
-
- Teicher BA, Herman TS, Holden SA, Wang Y, Pfeffer MR, Crawford JW, Frei E., III Tumor resistance to alkylating agents conferred by mechanisms operative only in vivo. Science. 1990;247:1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
