The Escherichia coli Ada protein can interact with two distinct determinants in the sigma70 subunit of RNA polymerase according to promoter architecture: identification of the target of Ada activation at the alkA promoter
- PMID: 10049384
- PMCID: PMC93542
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.5.1524-1529.1999
The Escherichia coli Ada protein can interact with two distinct determinants in the sigma70 subunit of RNA polymerase according to promoter architecture: identification of the target of Ada activation at the alkA promoter
Abstract
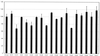
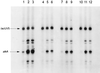
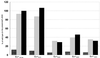
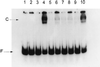
The methylated form of the Ada protein (meAda) activates transcription from the Escherichia coli ada, aidB, and alkA promoters with different mechanisms. In this study we identify amino acid substitutions in region 4 of the RNA polymerase subunit sigma70 that affect Ada-activated transcription at alkA. Substitution to alanine of residues K593, K597, and R603 in sigma70 region 4 results in decreased Ada-dependent binding of RNA polymerase to the alkA promoter in vitro and impairs alkA transcription both in vivo and in vitro, suggesting that these residues define a determinant for meAda-sigma70 interaction. In a previous study (P. Landini, J. A. Bown, M. R. Volkert, and S. J. W. Busby, J. Biol. Chem. 273:13307-13312, 1998), we showed that a set of negatively charged amino acids in sigma70 region 4 is involved in meAda-sigma70 interaction at the ada and aidB promoters. However, the alanine substitutions of positively charged residues K593, K597, and R603 do not affect meAda-dependent transcription at ada and aidB. Unlike the sigma70 amino acids involved in the interaction with meAda at the ada and aidB promoters, K593, K597, and R603 are not conserved in sigmaS, an alternative sigma subunit of RNA polymerase mainly expressed during the stationary phase of growth. While meAda is able to promote transcription by the sigmaS form of RNA polymerase (EsigmaS) at ada and aidB, it fails to do so at alkA. We propose that meAda can activate transcription at different promoters by contacting distinct determinants in sigma70 region 4 in a manner dependent on the location of the Ada binding site.
Figures

References
-
- Akimaru H, Sakumi K, Yoshikai T, Anai M, Sekiguchi M. Positive and negative regulation of transcription by a cleavage product of Ada protein. J Mol Biol. 1990;216:261–273. - PubMed
-
- Artsimovich I, Murakami K, Ishihama A, Howe M M. Transcription activation by the bacteriophage Mu Mor protein requires the C-terminal regions of both α and ς70 subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32343–32348. - PubMed
-
- Baikalov I, Schroeder I, Kaczor-Grzeskowiak M, Grzeskowiak K, Gunsalus R, Dickerson R. Structure of the Escherichia coli response regulator NarL. Biochemistry. 1996;35:11053–11061. - PubMed
-
- Busby S, Ebright R H. Transcription activation at class II CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:853–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

