Purification and characterization of a novel peroxidase from Geotrichum candidum dec 1 involved in decolorization of dyes
- PMID: 10049859
- PMCID: PMC91140
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.3.1029-1035.1999
Purification and characterization of a novel peroxidase from Geotrichum candidum dec 1 involved in decolorization of dyes
Abstract
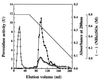
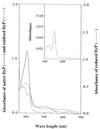
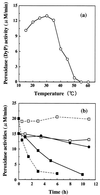
A peroxidase (DyP) involved in the decolorization of dyes and produced by the fungus strain Geotrichum candidum Dec 1 was purified. DyP, a glycoprotein, is glycosylated with N-acetylglucosamine and mannose (17%) and has a molecular mass of 60 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of 3.8. The absorption spectrum of DyP exhibited a Soret band at 406 nm corresponding to a hemoprotein, and its Na2S2O4-reduced form revealed a peak at 556 nm that indicates the presence of a protoheme as its prosthetic group. Nine of the 21 types of dyes that were decolorized by Dec 1 cells were decolorized by DyP; in particular, anthraquinone dyes were highly decolorized. DyP also oxidized 2,6-dimethoxyphenol and guaiacol but not veratryl alcohol. The optimal temperature for DyP activity was 30 degrees C, and DyP activity was stable even after incubation at 50 degrees C for 11 h.
Figures

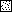 ——
—— ), DyP at 50°C (●——●),
DyP at 60°C (▪——▪), HRP at 40°C (
), DyP at 50°C (●——●),
DyP at 60°C (▪——▪), HRP at 40°C ( - - -
- - - ), and HRP at 60°C
(▪- - -▪).
), and HRP at 60°C
(▪- - -▪).
References
-
- Backa S, Gierer J, Reitberger T, Nilsson T. Hydroxyl radical activity associated with the growth of white-rot fungi. Holzforschung. 1993;47:181–187.
-
- Banat I M, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R. Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents. A review. Biores Technol. 1996;58:217–227.
-
- Bordeleau L M, Bartha R. Biochemical transformations of herbicide-derived anilines: purification and characterization of causative enzymes. Can J Microbiol. 1972;18:1865–1871. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

