Isolation from estuarine sediments of a Desulfovibrio strain which can grow on lactate coupled to the reductive dehalogenation of 2,4, 6-tribromophenol
- PMID: 10049873
- PMCID: PMC91154
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.3.1133-1140.1999
Isolation from estuarine sediments of a Desulfovibrio strain which can grow on lactate coupled to the reductive dehalogenation of 2,4, 6-tribromophenol
Abstract
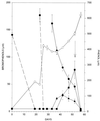
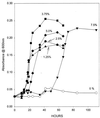
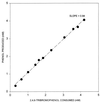
Strain TBP-1, an anaerobic bacterium capable of reductively dehalogenating 2,4,6-tribromophenol to phenol, was isolated from estuarine sediments of the Arthur Kill in the New York/New Jersey harbor. It is a gram-negative, motile, vibrio-shaped, obligate anaerobe which grows on lactate, pyruvate, hydrogen, and fumarate when provided sulfate as an electron acceptor. The organism accumulates acetate when grown on lactate and sulfate, contains desulfoviridin, and will not grow in the absence of NaCl. It will not utilize acetate, succinate, propionate, or butyrate for growth via sulfate reduction. When supplied with lactate as an electron donor, strain TBP-1 will utilize sulfate, sulfite, sulfur, and thiosulfate for growth but not nitrate, fumarate, or acrylate. This organism debrominates 2-, 4-, 2,4-, 2,6-, and 2,4,6-bromophenol but not 3- or 2,3-bromophenol or monobrominated benzoates. It will not dehalogenate monochlorinated, fluorinated, or iodinated phenols or chlorinated benzoates. Together with its physiological characteristics, its 16S rRNA gene sequence places it in the genus Desulfovibrio. The average growth yield of strain TBP-1 grown on a defined medium supplemented with lactate and 2,4,6-bromophenol is 3.71 mg of protein/mmol of phenol produced, and the yield was 1.42 mg of protein/mmol of phenol produced when 4-bromophenol was the electron acceptor. Average growth yields (milligrams of protein per millimole of electrons utilized) for Desulfovibrio sp. strain TBP-1 grown with 2,4,6-bromophenol, 4-bromophenol, or sulfate are 0.62, 0.71, and 1.07, respectively. Growth did not occur when either lactate or 2,4,6-bromophenol was omitted from the growth medium. These results indicate that Desulfovibrio sp. strain TBP-1 is capable of growth via halorespiration.
Figures


References
-
- Bouchard B, Beaudet R, Villemur R, McSween G, Lepine F, Bisaillon J G. Isolation and characterization of Desulfitobacterium frappieri sp. nov., an anaerobic bacterium which reductively dechlorinates pentachlorophenol to 3-chlorophenol. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:1010–1015. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen N, Ahring B K. Desulfitobacterium hafniense sp. nov., an anaerobic, reductively dechlorinating bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:442–448.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

