A comparison of an A1 adenosine receptor agonist (CVT-510) with diltiazem for slowing of AV nodal conduction in guinea-pig
- PMID: 10051130
- PMCID: PMC1565791
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702287
A comparison of an A1 adenosine receptor agonist (CVT-510) with diltiazem for slowing of AV nodal conduction in guinea-pig
Abstract
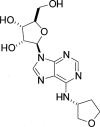
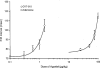
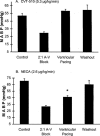
1. The purpose of this study was to compare the pharmacological properties (i.e. the AV nodal depressant, vasodilator, and inotropic effects) of two AV nodal blocking agents belonging to different drug classes; a novel A1 adenosine receptor (A1 receptor) agonist, N-(3(R)-tetrahydrofuranyl)-6-aminopurine riboside (CVT-510), and the prototypical calcium channel blocker diltiazem. 2. In the atrial-paced isolated heart, CVT-510 was approximately 5 fold more potent to prolong the stimulus-to-His bundle (S-H interval), a measure of slowing AV nodal conduction (EC50 = 41 nM) than to increase coronary conductance (EC50 = 200 nM). At concentrations of CVT-510 (40 nM) and diltiazem (1 microM) that caused equal prolongation of S-H interval (approximately 10 ms), diltiazem, but not CVT-510, significantly reduced left ventricular developed pressure (LVP) and markedly increased coronary conductance. CVT-510 shortened atrial (EC50 = 73 nM) but not the ventricular monophasic action potentials (MAP). 3. In atrial-paced anaesthetized guinea-pigs, intravenous infusions of CVT-510 and diltiazem caused nearly equal prolongations of P-R interval. However, diltiazem, but not CVT-510, significantly reduced mean arterial blood pressure. 4. Both CVT-510 and diltiazem prolonged S-H interval, i.e., slowed AV nodal conduction. However, the A1 receptor-selective agonist CVT-510 did so without causing the negative inotropic, vasodilator, and hypotensive effects associated with diltiazem. Because CVT-510 did not affect the ventricular action potential, it is unlikely that this agonist will have a proarrythmic action in ventricular myocardium.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The cardiac effects of a novel A1-adenosine receptor agonist in guinea pig isolated heart.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Dec;271(3):1371-82. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994. PMID: 7996449
-
Electrophysiologic effects of a novel selective adenosine A1 agonist (CVT-510) on atrioventricular nodal conduction in humans.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Jul;6(3):237-45. doi: 10.1177/107424840100600304. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11584330
-
A partial agonist of the A(1)-adenosine receptor selectively slows AV conduction in guinea pig hearts.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001 Jan;280(1):H334-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.1.H334. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11123249
-
Pharmacological basis for the therapeutic applications of slow-channel blocking drugs.Angiology. 1982 Aug;33(8):492-515. doi: 10.1177/000331978203300802. Angiology. 1982. PMID: 7051905 Review.
-
CVT-510: a selective A1 adenosine receptor agonist.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Winter;21(4):277-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00122.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 14647532 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine A1 and A3 Receptors: Distinct Cardioprotection.Drug Dev Res. 2001 Jan-Feb;52(1-2):366-378. doi: 10.1002/ddr.1136. Drug Dev Res. 2001. PMID: 39741902 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine and ischemic preconditioning.Curr Pharm Des. 1999 Dec;5(12):1029-41. Curr Pharm Des. 1999. PMID: 10607860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perspective on rate control in the treatment of atrial fibrillation.Clin Cardiol. 2004 Mar;27(3):121-4. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960270304. Clin Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15049376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninvasive Assessment of Atrioventricular Nodal Function: Effect of Rate-Control Drugs during Atrial Fibrillation.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015 Nov;20(6):534-41. doi: 10.1111/anec.12253. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015. PMID: 25545540 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic potency of A1 adenosine receptor antagonists in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, current status and perspectives.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 24;51(1):358. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09246-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38400849 Review.
References
-
- BELARDINELLI L., SHRYOCK J.C., SNOWDY S., ZHANG Y., MONOPOLI A., LOZZA G., ONGINI E., OLSSON R.A., DENNIS D.M. The A2A adenosine receptor mediates coronary vasodilation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;284:1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- BELARDINELLI L., SHRYOCK J.C., SONG Y., WANG D., SRINIVAS M. Ionic basis of the electrophysiological actions of adenosine on cardiomyocytes. FASEB J. 1995;9:359–365. - PubMed
-
- BROWN J.N., THORNE P.R., NUTTALL A.L. Blood pressure and other physiological responses in awake and anesthetized guinea pigs. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1989;39:142–148. - PubMed
-
- CLEMO H.F., BELARDINELLI L. Effect of adenosine on atrioventricular conduction. I. Site and characterization of adenosine action in the guinea pig atrioventricular node. Circ. Res. 1986;59:427–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

