[3H]-Mesulergine labels 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum but not rat jejunum
- PMID: 10051134
- PMCID: PMC1565797
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702293
[3H]-Mesulergine labels 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum but not rat jejunum
Abstract
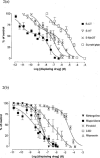
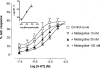
1. The primary aim of this investigation was to determine whether binding sites corresponding to the 5-HT7 receptor could be detected in smooth muscle of the rat jejunum. Binding studies in rat brain (whole brain minus cerebellum) and guinea-pig ileal longitudinal muscle were also undertaken in order to compare the binding characteristics of these tissues. Studies were performed using [3H]-mesulergine, as it has a high affinity for 5-HT7 receptors. 2. In the rat brain and guinea-pig ileum, pKD values for [3H]-mesulergine of 8.0 +/- 0.04 and 7.9 +/- 0.11 (n = 3) and Bmax values of 9.9 +/- 0.3 and 21.5 +/- 4.9 fmol mg(-1) protein were obtained respectively, but no binding was detected in the rat jejunum. [3H]-mesulergine binding in the rat brain and guinea-pig ileum was displaced with the agonists 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) > 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) > or = 5-methoxytryptamine (5-MeOT) > sumatriptan and the antagonists risperidone > or = LSD > or = metergoline > ritanserin > > pindolol. 3. Despite the lack of [3H]-mesulergine binding in the rat jejunum, functional studies undertaken revealed a biphasic contractile response to 5-HT which was partly blocked by ondansetron (1 microM). The residual response was present in over 50% of tissues studied and was found to be inhibited by risperidone > LSD > metergoline > mesulergine = ritanserin > pindolol, but was unaffected by RS 102221 (3 microM), cinanserin (30 nM), yohimbine (0.1 microM) and GR 113808 (1 microM). In addition, the agonist order of potency was 5-CT > 5-HT > 5-MeOT > sumatriptan. 4. In conclusion, binding studies performed with [3H]-mesulergine were able to detect 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum, but not in rat jejunum, where a functional 5-HT7-like receptor was present.
Figures
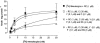

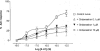
References
-
- BAKER L.P., NIELSEN M.D., IMPEY S., METCALF M.A., POSER S.W., CHAN G., OBRIETAN K., HAMBLIN M.W., STORM D.R. Stimulation of type I and type 8 Ca2+ calmodulin-sensitive adenylyl cyclases by the GS-coupled 5-hydroxytryptamine subtype 5-HT7A receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:17469–17476. - PubMed
-
- BARD J.A., ZGOMBICK J., ADHAM N., VAYSSE P., BRANCHEK T.A., WEINSHANK R.L. Cloning of a novel serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;31:23422–23426. - PubMed
-
- BOESS F.G., MARTIN I.L. Review: molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacol. 1994;33:275–317. - PubMed
-
- BONHAUS D.W., WEINHARDT K.K., TAYLOR M., DESOUZA A., MCNEELEY P.M., SZCZEPANSKI K., FONTANA D.J., TRINH J., ROCHA C.L., DAWSON M.W., FLIPPIN L.A., EGLEN R.M. RS-102221: a novel high affinity and selective, 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacol. 1997;36:621–629. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

