Acetylcholine-induced relaxation in blood vessels from endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice
- PMID: 10051139
- PMCID: PMC1565804
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702300
Acetylcholine-induced relaxation in blood vessels from endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice
Abstract
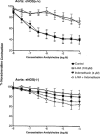
1. Isometric tension was recorded in isolated rings of aorta, carotid, coronary and mesenteric arteries taken from endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice (eNOS(-/-) mice) and the corresponding wild-type strain (eNOS(+/+) mice). The membrane potential of smooth muscle cells was measured in coronary arteries with intracellular microelectrodes. 2. In the isolated aorta, carotid and coronary arteries from the eNOS(+/+) mice, acetylcholine induced an endothelium-dependent relaxation which was inhibited by N(omega)-L-nitro-arginine. In contrast, in the mesenteric arteries, the inhibition of the cholinergic relaxation required the combination of N(omega)-L-nitro-arginine and indomethacin. 3. The isolated aorta, carotid and coronary arteries from the eNOS(-/-) mice did not relax in response to acetylcholine. However, acetylcholine produced an indomethacin-sensitive relaxation in the mesenteric artery from eNOS(-/-) mice. 4. The resting membrane potential of smooth muscle cells from isolated coronary arteries was significantly less negative in the eNOS(-/-) mice (-64.8 +/- 1.8 mV, n = 20 and -58.4 +/- 1.9 mV, n = 17, for eNOS(+/+) and eNOS(-/-) mice, respectively). In both strains, acetylcholine, bradykinin and substance P did not induce endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizations whereas cromakalim consistently produced hyperpolarizations (- 7.9 +/- 1.1 mV, n = 8 and -13.8 +/- 2.6 mV, n = 4, for eNOS(+/+) and eNOS(-/-) mice, respectively). 5. These findings demonstrate that in the blood vessels studied: (1) in the eNOS(+/+) mice, the endothelium-dependent relaxations to acetylcholine involve either NO or the combination of NO plus a product of cyclo-oxygenase but not EDHF; (2) in the eNOS(-/-) mice, NO-dependent responses and EDHF-like responses were not observed. In the mesenteric arteries acetylcholine releases a cyclo-oxygenase derivative.
Figures




References
-
- BAUERSACHS J., LISCHKE V., BUSSE R., HECKER M.Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in the coronary microcirculation Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor 1996Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Harwood Academic Publishers; 211–216.ed. Vanhoutte P.M., pp
-
- BERTHIAUME N., HESS F., CHEN A., REGOLI D., D'ORLEANS-JUSTE P. Pharmacology of kinins in the arterial and venous mesenteric bed of normal and B2 knockout transgenic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;333:55–61. - PubMed
-
- BEVERELLI F., BEA M.L., PUYBASSET L., GIUDICELLI J.F., BERDEAUX A. Chronic inhibition of NOS enhances the production of prostacyclin in coronary arteries through upregulation of the cyclo-oxygenase type 1 isoform. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997;11:252–259. - PubMed
-
- CAYATTE A.J., PALACINO J.J., HORTEN K., COHEN R.A. Chronic inhibition of nitric oxide production accelerates neointima formation and impairs endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1994;14:753–759. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

