Mibefradil (Ro 40-5967) inhibits several Ca2+ and K+ currents in human fusion-competent myoblasts
- PMID: 10051142
- PMCID: PMC1565812
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702321
Mibefradil (Ro 40-5967) inhibits several Ca2+ and K+ currents in human fusion-competent myoblasts
Abstract
1. The effect of mibefradil (Ro 40-5967), an inhibitor of T-type Ca2+ current (I(Ca)(T)), on myoblast fusion and on several voltage-gated currents expressed by fusion-competent myoblasts was examined. 2. At a concentration of 5 microM, mibefradil decreases myoblast fusion by 57%. At this concentration, the peak amplitudes of I(Ca)(T) and L-type Ca2+ current (I(Ca)(L)) measured in fusion-competent myoblasts are reduced by 95 and 80%, respectively. The IC50 of mibefradil for I(Ca)(T) and I(Ca)(L) are 0.7 and 2 microM, respectively. 3. At low concentrations, mibefradil increased the amplitude of I(Ca)(L) with respect to control. 4. Mibefradil blocked three voltage-gated K+ currents expressed by human fusion-competent myoblasts: a delayed rectifier K+ current, an ether-à-go-go K+ current, and an inward rectifier K+ current, with a respective IC50 of 0.3, 0.7 and 5.6 microM. 5. It is concluded that mibefradil can interfere with myoblast fusion, a mechanism fundamental to muscle growth and repair, and that the interpretation of the effect of mibefradil in a given system should take into account the action of this drug on ionic currents other than Ca2+ currents.
Figures


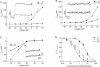
Similar articles
-
Voltage-dependent blockade of diverse types of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the Ca2+ channel antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40-5967).Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Sep;48(3):540-9. Mol Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7565636
-
Inhibition by mibefradil, a novel calcium channel antagonist, of Ca(2+)- and volume-activated Cl- channels in macrovascular endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;121(3):547-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701140. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9179399 Free PMC article.
-
Mibefradil (Ro 40-5967) blocks multiple types of voltage-gated calcium channels in cultured rat spinal motoneurones.Cell Calcium. 1997 Oct;22(4):299-311. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(97)90068-3. Cell Calcium. 1997. PMID: 9481480
-
Cardiovascular T-type calcium channels: physiological and pharmacological significance.J Hypertens Suppl. 1997 Dec;15(5):S9-15. J Hypertens Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9481611 Review.
-
Discovery and main pharmacological properties of mibefradil (Ro 40-5967), the first selective T-type calcium channel blocker.J Hypertens Suppl. 1997 Dec;15(5):S17-25. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199715055-00004. J Hypertens Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9481612 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and experimental insight into pathophysiology, comorbidity and therapy of absence seizures.Brain. 2020 Aug 1;143(8):2341-2368. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa072. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32437558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-type alpha 1H Ca2+ channels are involved in Ca2+ signaling during terminal differentiation (fusion) of human myoblasts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7627-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.13.7627. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10861024 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation and pharmacology of low voltage-activated ("T-Type") calcium channels.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003 Dec;35(6):577-98. doi: 10.1023/b:jobb.0000008025.65675.37. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003. PMID: 15000521 Review.
-
T-Type Calcium Channel: A Privileged Gate for Calcium Entry and Control of Adrenal Steroidogenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 May 20;7:43. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00043. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27242667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-type calcium channels in synaptic plasticity.Channels (Austin). 2017 Mar 4;11(2):121-139. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2016.1238992. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Channels (Austin). 2017. PMID: 27653665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BAROFFIO A., AUBRY J.P., KAELIN A., KRAUSE R.M., HAMANN M., BADER C.R. Purification of human muscle satellite cells by flow cytometry. Muscle Nerve. 1993;16:498–505. - PubMed
-
- BAROFFIO A., HAMANN M., BERNHEIM L., BOCHATON-PIALLAT M.L., GABBIANI G., BADER C.R. Identification of self-renewing myoblasts in the progeny of single human muscle satellite cells. Differentiation. 1996;60:47–57. - PubMed
-
- CLOZEL J.P., ERTEL E.A., ERTEL S.I. Discovery and main pharmacological properties of mibefradil (Ro 40-5967), the first selective T-type calcium channel blocker. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1997;15:S17–S25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

