Effects of phrixotoxins on the Kv4 family of potassium channels and implications for the role of Ito1 in cardiac electrogenesis
- PMID: 10051143
- PMCID: PMC1565788
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702283
Effects of phrixotoxins on the Kv4 family of potassium channels and implications for the role of Ito1 in cardiac electrogenesis
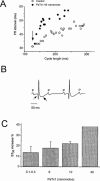
Abstract
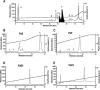
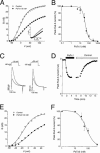
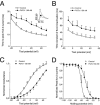
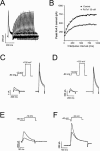
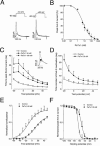
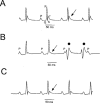
1. In the present study, two new peptides, phrixotoxins PaTx1 and PaTx2 (29-31 amino acids), which potently block A-type potassium currents, have been purified from the venom of the tarantula Phrixotrichus auratus. 2. Phrixotoxins specifically block Kv4.3 and Kv4.2 currents that underlie I(to1), with an 5 < IC50 < 70 nM, by altering the gating properties of these channels. 3. Neither are the Shaker (Kv1), Shab (Kv2) and Shaw (Kv3) subfamilies of currents, nor HERG, KvLQT1/IsK, inhibited by phrixotoxins which appear specific of the Shal (Kv4) subfamily of currents and also block I(to1) in isolated murine cardiomyocytes. 4. In order to evaluate the physiological consequences of the Ito1 inhibition, mice were injected intravenously with PaTx1, which resulted in numerous transient cardiac adverse reactions including the occurrence of premature ventricular beats, ventricular tachycardia and different degrees of atrioventricular block. 5. The analysis of the mouse electrocardiogram showed a dose-dependent prolongation of the QT interval, chosen as a surrogate marker for their ventricular repolarization, from 249 +/- 11 to 265 +/- 8 ms (P < 0.05). 6. It was concluded that phrixotoxins, are new and specific blockers of Kv4.3 and Kv4.2 potassium currents, and hence of I(to1) that will enable further studies of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 channel and/or I(to1) expression.
Figures

References
-
- AIYAR J., WITHKA J.M., RIZZI J.P., SINGLETON D.H., ANDREWS G.C., LIN W., BOYD J., HANSON D.C., SIMON M., DETHLEFS B., LEE C., HALL J.E., GUTMAN G.A., CHANDY K.G. Topology of the pore-region of a K+ channel revealed by the NMR-derived structures of scorpions toxins. Neuron. 1995;15:1169–1181. - PubMed
-
- ATTALI B. Ion channels A new wave for heart rhythms. Nature. 1996;384:24–25. - PubMed
-
- BAGETTA G., NISTICO G., DOLLY J.O. Production of seizures and brain damage in rats by α-dendrotoxin, a selective K+ channel blocker. Neurosci. Lett. 1992;139:24–40. - PubMed
-
- BALDWIN T.J., TSAUR M.-L., LOPEZ G.A., JAN Y.N., JAN L.Y. Characterization of a mammalian cDNA for an inactivating voltage-sensitive K+ channel. Neuron. 1991;7:471–483. - PubMed
-
- BARHANIN J., LESAGE F., GUILLEMARE E., FINK M., LAZDUNSKI M., ROMEY G. KvLQT1 and Isk (minK) proteins associate to form the IKs cardiac potassium current. Nature. 1996;384:78–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

