Modulation of acute and chronic inflammatory processes by cacospongionolide B, a novel inhibitor of human synovial phospholipase A2
- PMID: 10051149
- PMCID: PMC1565805
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702302
Modulation of acute and chronic inflammatory processes by cacospongionolide B, a novel inhibitor of human synovial phospholipase A2
Abstract
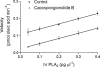
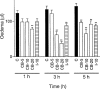
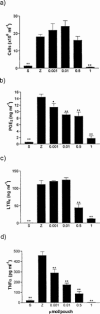
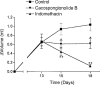
1. Cacospongionolide B is a novel marine metabolite isolated from the sponge Fasciospongia cavernosa. In in vitro studies, this compound inhibited phospholipase A2 (PLA2), showing selectivity for secretory PLA2 (sPLA2) versus cytosolic PLA2 (cPLA2), and its potency on the human synovial enzyme (group II) was similar to that of manoalide. 2. This activity was confirmed in vivo in the 8 h zymosan-injected rat air pouch, on the secretory enzyme accumulating in the pouch exudate. Cacospongionolide B, that is bioavailable when is given orally, reduced the elevated levels of sPLA2 present in paw homogenates of rats with adjuvant arthritis. 3. This marine metabolite showed topical anti-inflammatory activity on the mouse ear oedema induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol acetate (TPA) and decreased carrageenin paw oedema in mice after oral administration of 5, 10 or 20 mg kg(-1). 4. In the mouse air pouch injected with zymosan, cacospongionolide B administered into the pouch, induced a dose-dependent reduction in the levels of eicosanoids and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) in the exudates 4 h after the stimulus. It also had a weak effect on cell migration. 5. The inflammatory response of adjuvant arthritis was reduced by cacospongionolide B, which did not significantly affect eicosanoid levels in serum, paw or stomach homogenates and did not induce toxic effects. 6 Cacospongionolide B is a new inhibitor of sPLA2 in vitro and in vivo, with anti-inflammatory properties in acute and chronic inflammation. This marine metabolite was active after oral administration and able to modify TNFalpha levels, and may offer an interesting approach in the search for new anti-inflammatory agents.
Figures

References
-
- ABE T., SAKAMOTO K., KAMOHARA H., HIRANO Y., KUWAHARA N., OGAWA M. Group II phospholipase A2 is increased in peritoneal and pleural effusions in patients with various types of cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 1997;74:245–250. - PubMed
-
- AMANDI-BURGERMEISTER E., TIBES U., KAISER B.M., FRIEBE W.G., SCHEUER W.V. Suppression of cytokine synthesis, integrin expression and chronic inflammation by inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;326:237–250. - PubMed
-
- ARBIBE L., VIAL D., ROSINSKI-CHUPIN I., HAVET N., HUERRE M., VARGAFTIG B.B., TOUQUI L. Endotoxin induces expression of type II phospholipase A2 in macrophages during acute lung injury in guinea pigs. Involvement of TNF-α in lipopolysaccharide-induced type II phospholipase A2 synthesis. J. Immunol. 1997;159:391–400. - PubMed
-
- BALBOA M.A., BALSINDE J., WINSTEAD M.V., TISCHFIELD J.A., DENNIS E.A. Novel group V phospholipase A2 involved in arachidonic acid mobilization in murine P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:32381–32384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

