Growth-inhibitory effect of cyclic GMP- and cyclic AMP-dependent vasodilators on rat vascular smooth muscle cells: effect on cell cycle and cyclin expression
- PMID: 10051155
- PMCID: PMC1565807
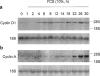
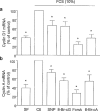
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702305
Growth-inhibitory effect of cyclic GMP- and cyclic AMP-dependent vasodilators on rat vascular smooth muscle cells: effect on cell cycle and cyclin expression
Abstract
1. The possibility that the antiproliferative effect of cyclic GMP- and cyclic AMP-dependent vasodilators involves an impaired progression of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) through the cell cycle and expression of cyclins, which in association with the cyclin-dependent kinases control the transition between the distinct phases of the cell cycle, was examined. 2. FCS (10%) stimulated the transition of quiescent VSMC from the G0/G1 to the S phase (maximum within 18-24 h and then to the G2/M phase (maximum within 22-28 h). Sodium nitroprusside and 8-Br-cyclic GMP, as well as forskolin and 8-Br-cyclic AMP markedly reduced the percentage of cells in the S phase after FCS stimulation. 3. FCS stimulated the low basal protein expression of cyclin D1 (maximum within 8-24 h) and E (maximum within 8-38 h) and of cyclin A (maximum within 14-30 h). The stimulatory effect of FCS on cyclin D1 and A expression was inhibited, but that of cyclin E was only minimally affected by the vasodilators. 4. FCS increased the low basal level of cyclin D1 mRNA after a lag phase of 2 h and that of cyclin A after 12 h. The vasodilators significantly reduced the FCS-stimulated expression of cyclin D1 and A mRNA. 5. These findings indicate that cyclic GMP- and cyclic AMP-dependent vasodilators inhibit the proliferation of VSMC by preventing the progression of the cell cycle from the G0/G1 into the S phase, an effect which can be attributed to the impaired expression of cyclin D1 and A.
Figures






References
-
- ABELL T.J., RICHARDS A.M., IKRAM H., ESPINIER E.A., YANDLE T. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;160:1392–1396. - PubMed
-
- BARLAT I., HENGLEIN B., PLET A., LAMB N., FERNANDEZ A., MCKENZIE F., POUYSSÉGUR J., VIÉ A., BLANCHARD J.M. TGF-β1 and cyclic AMP attenuate cyclin A gene transcription via a cyclic AMP responsive element through independent pathways. Oncogene. 1995;11:1309–1318. - PubMed
-
- BEAVO J.A., REIFSYNDER D.H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990;11:150–155. - PubMed
-
- BUSSE R., FLEMING I. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. J. Vasc. Res. 1996;331:181–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

