Properties and functional roles of hyperpolarization-gated currents in guinea-pig retinal rods
- PMID: 10066907
- PMCID: PMC2269198
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.813ab.x
Properties and functional roles of hyperpolarization-gated currents in guinea-pig retinal rods
Abstract
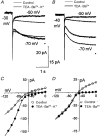
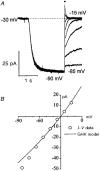
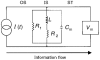
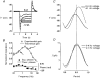
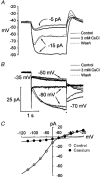
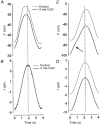
1. The inward rectification induced by membrane hyperpolarization was studied in adult guinea-pig rods by the perforated-patch-clamp technique. 2. CsCl blocked the rectification observed in both voltage- and current-clamp recordings at voltages negative to -60 mV, while BaCl2 blocked the inward relaxation observed at voltages positive to -60 mV. The current activated at -90 mV had a low selectivity between sodium and potassium and reversed at -31.0 mV. 3. These observations suggest that two inward rectifiers are present in guinea-pig rods: a hyperpolarization-activated (Ih) and a hyperpolarization-deactivated (Ikx) current. The functional roles of Ih and Ikx were evaluated by stimulating rods with currents sinusoidally modulated in time. 4. Rods behave like bandpass amplifiers, with a peak amplification of 1.5 at about 2 Hz. For hyperpolarizations that mainly gate Ikx, amplification and phase shifts are fully accounted for by a rod membrane analogue model that includes an inductance. For hyperpolarizations that also gate Ih, a harmonic distortion became apparent. 5. Bandpass filtering and amplification of rod signals, associated with Ih and Ikx gating by membrane hyperpolarization, are strategically located to extend, beyond the limits imposed by the slow phototransductive cascade, the temporal resolution of signals spreading to the rod synapse.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

