Adenosine inhibits the transfected Na+-H+ exchanger NHE3 in Xenopus laevis renal epithelial cells (A6/C1)
- PMID: 10066908
- PMCID: PMC2269197
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.829ab.x
Adenosine inhibits the transfected Na+-H+ exchanger NHE3 in Xenopus laevis renal epithelial cells (A6/C1)
Abstract
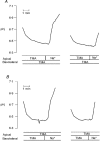
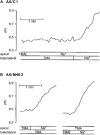
1. Adenosine influences the vectorial transport of Na+ and HCO3- across kidney epithelial cells. However, its action on effector proteins, such as the Na+-H+ exchanger NHE3, an epithelial brush border isoform of the Na+-H+ exchanger (NHE) gene family, is not yet defined. 2. The present study was conducted in Xenopus laevis distal nephron A6 epithelia which express both an apical adenosine receptor of the A1 type (coupled to protein kinase C (PKC)) and a basolateral receptor of the A2 type (coupled to protein kinase A (PKA)). The untransfected A6 cell line expresses a single NHE type (XNHE) which is restricted to the basolateral membrane and which is activated by PKA. 3. A6 cell lines were generated which express exogenous rat NHE3. Measurements of side-specific pHi recovery from acid loads in the presence of HOE694 (an inhibitor with differential potency towards individual NHE isoforms) detected an apical resistant Na+-H+ exchange only in transfected cell lines. The sensitivity of the basolateral NHE to HOE694 was unchanged, suggesting that exogenous NHE3 was restricted to the apical membrane. 4. Stimulation of the apical A1 receptor with N 6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) inhibited both apical NHE3 and basolateral XNHE. These effects were mimicked by the addition of the protein kinase C (PKC) activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and partially prevented by the PKC inhibitor calphostin C which also blocked the effect of PMA. 5. Stimulation of the basolateral A2 receptor with CPA inhibited apical NHE3 and stimulated basolateral XNHE. These effects were mimicked by 8-bromo-cAMP and partially prevented by the PKA inhibitor H89 which entirely blocked the effect of 8-bromo-cAMP. 6. In conclusion, CPA inhibits rat NHE3 expressed apically in A6 epithelia via both the apical PKC-coupled A1 and the basolateral PKA-coupled A2 adenosine receptors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Molecular aspects of acute inhibition of Na(+)-H(+) exchanger NHE3 by A(2)-adenosine receptor agonists.J Physiol. 2002 Jun 1;541(Pt 2):529-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013438. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12042357 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the transfected Na+/H+-exchanger NHE3 in MDCK cells by vasotocin.Pflugers Arch. 1997 May;434(1):123-31. doi: 10.1007/s004240050372. Pflugers Arch. 1997. PMID: 9094265
-
Extracellular adenine nucleotides regulate Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 activity in A6-NHE3 transfectants by a cAMP/PKA-dependent mechanism.J Membr Biol. 2002 Aug 1;188(3):249-59. doi: 10.1007/s00232-001-0189-8. J Membr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12181615 Free PMC article.
-
Na+,K+ pump and Na+-coupled ion carriers in isolated mammalian kidney epithelial cells: regulation by protein kinase C.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999 May;77(5):305-19. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10535680 Review.
-
Short-term regulation of NHE3 by EGF and protein kinase C but not protein kinase A involves vesicle trafficking in epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;915:30-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05221.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193592 Review.
Cited by
-
Caffeine-induced diuresis and natriuresis is independent of renal tubular NHE3.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):F1409-20. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00129.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25925253 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms for apical ATP effects on intracellular pH in human bronchial epithelium.J Physiol. 2002 Aug 15;543(Pt 1):13-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.015180. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12181278 Free PMC article.
-
Luminal Na(+)/H (+) exchange in the proximal tubule.Pflugers Arch. 2009 May;458(1):5-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0595-1. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 18853182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low salt intake increases adenosine type 1 receptor expression and function in the rat proximal tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):F37-41. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00061.2008. Epub 2008 May 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18480183 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular aspects of acute inhibition of Na(+)-H(+) exchanger NHE3 by A(2)-adenosine receptor agonists.J Physiol. 2002 Jun 1;541(Pt 2):529-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013438. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12042357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amemiya M, Loffing J, Lötscher M, Kaissling B, Alpern RJ, Moe OW. Expression of NHE-3 in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. Kidney International. 1995;48:1206–1215. - PubMed
-
- Amemiya M, Yamaji Y, Cano A, Moe OW, Alpern RJ. Acid incubation increases NHE-3 mRNA abundance in OKP cells. American Journal of Physiology. 1995;269:C126–133. - PubMed
-
- Azarani A, Goltzman D, Orlowski J. Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide inhibit the apical Na+/H+ exchanger NHE-3 isoform in renal cells (OK) via a dual signaling cascade involving protein kinase A and C. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270:20004–20010. 10.1074/jbc.270.34.20004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biemesderfer D, Rutherford PA, Nagy T, Pizzonia JH, Abu-Alfi AK, Aronson P. Monoclonal antibodies for high-resolution localization of NHE3 in adult and neonatal rat kidney. American Journal of Physiology. 1997;273:F289–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

