Phosphorylation of tyrosine 992, 1068, and 1086 is required for conformational change of the human epidermal growth factor receptor c-terminal tail
- PMID: 10069801
- PMCID: PMC25185
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.525
Phosphorylation of tyrosine 992, 1068, and 1086 is required for conformational change of the human epidermal growth factor receptor c-terminal tail
Abstract
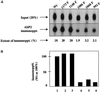
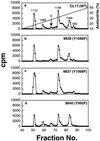
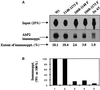
We reported previously that a conformation-specific antibody, Ab P2, to a 16-amino acid peptide (Glu-Gly-Tyr-Lys-Lys-Lys-Tyr-Gln-Gln-Val-Asp-Glu-Glu-Phe-Leu-Arg) of the cytoplasmic domain of the beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor also recognizes the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. Although the antibody is not directed to phosphotyrosine, it recognizes in immunoprecipitation the activated and hence phosphorylated form of both receptors. In P2 peptide, there are two tripeptide sequences, Asp-Glu-Glu and Tyr-Gln-Gln, that are also present in the EGF receptor. Our present studies using either EGF receptor C-terminal deletion mutants or point mutations (Tyr-->Phe) and our previous studies on antibody inhibition by P2-derived peptides suggest that Gln-Gln in combination with Asp-Glu-Glu forms a high-affinity complex with Ab P2 and that such complex formation is dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. Of the five phosphate acceptor sites in the EGF receptor, clustered in the extreme C-terminal tail, phosphorylation of three tyrosine residues (992, 1068, and 1086) located between Asp-Glu-Glu and Gln-Gln is necessary for Ab P2 binding. In contrast, the acceptor sites Tyr 1173 and 1148 play no role in the conformation change. Asp-Glu-Glu and Gln-Gln are located 169 amino acids apart, and it is highly likely that the interactions among three negatively charged phosphotyrosine residues in the receptor C terminus may result in the bending of the peptide chain in such a way that these two peptides come close to each other to form an antibody-binding site. Such a possibility is also supported by our finding that receptor dephosphorylation results in complete loss of Ab P2-binding activity. In conclusion, we have identified a domain within the cytoplasmic part of the EGF receptor whose conformation is altered by receptor phosphorylation; furthermore, we have identified the tyrosine residues that positively regulate this conformation.
Figures

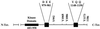

References
-
- Alvarez CV, Shon K-J, Miloso M, Beguinot L. Structural requirements of the epidermal growth factor receptor for tyrosine phosphorylation of esp8 and esp15, substrates lacking Src SH2 homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:16271–16276. - PubMed
-
- Biswas R, Basu M, Sen-Majumdar A, Das M. Intrapeptide autophosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor: regulation of kinase catalytic function by receptor dimerization. Biochemistry. 1985;24:3795–3802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

