High-affinity binding of the AP-1 adaptor complex to trans-golgi network membranes devoid of mannose 6-phosphate receptors
- PMID: 10069802
- PMCID: PMC25186
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.537
High-affinity binding of the AP-1 adaptor complex to trans-golgi network membranes devoid of mannose 6-phosphate receptors
Abstract
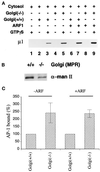
The GTP-binding protein ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) initiates clathrin-coat assembly at the trans-Goli network (TGN) by generating high-affinity membrane-binding sites for the AP-1 adaptor complex. Both transmembrane proteins, which are sorted into the assembling coated bud, and novel docking proteins have been suggested to be partners with GTP-bound ARF in generating the AP-1-docking sites. The best characterized, and probably the major transmembrane molecules sorted into the clathrin-coated vesicles that form on the TGN, are the mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs). Here, we have examined the role of the MPRs in the AP-1 recruitment process by comparing fibroblasts derived from embryos of either normal or MPR-negative animals. Despite major alterations to the lysosome compartment in the MPR-deficient cells, the steady-state distribution of AP-1 at the TGN is comparable to that of normal cells. Golgi-enriched membranes prepared from the receptor-negative cells also display an apparently normal capacity to recruit AP-1 in vitro in the presence of ARF and either GTP or GTPgammaS. The AP-1 adaptor is recruited specifically onto the TGN and not onto the numerous abnormal membrane elements that accumulate within the MPR-negative fibroblasts. AP-1 bound to TGN membranes from either normal or MPR-negative fibroblasts is fully resistant to chemical extraction with 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7, indicating that the adaptor binds to both membrane types with high affinity. The only difference we do note between the Golgi prepared from the MPR-deficient cells and the normal cells is that AP-1 recruited onto the receptor-lacking membranes in the presence of ARF1.GTP is consistently more resistant to extraction with Tris. Because sensitivity to Tris extraction correlates well with nucleotide hydrolysis, this finding might suggest a possible link between MPR sorting and ARF GAP regulation. We conclude that the MPRs are not essential determinants in the initial steps of AP-1 binding to the TGN but, instead, they may play a regulatory role in clathrin-coated vesicle formation by affecting ARF.GTP hydrolysis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 transiently activates high-affinity adaptor protein complex AP-1 binding sites on Golgi membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Jun;9(6):1323-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.6.1323. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9614177 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose 6-phosphate receptors and ADP-ribosylation factors cooperate for high affinity interaction of the AP-1 Golgi assembly proteins with membranes.J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 26;271(4):2162-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.4.2162. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8567674
-
Mannose 6-phosphate receptors regulate the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles in the TGN.J Cell Biol. 1997 Apr 21;137(2):335-45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.2.335. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9128246 Free PMC article.
-
Protein transport from the secretory to the endocytic pathway in mammalian cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):195-209. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00057-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714803 Review.
-
Receptor-mediated sorting of soluble vacuolar proteins: myths, facts, and a new model.J Exp Bot. 2016 Aug;67(15):4435-49. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw222. Epub 2016 Jun 4. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27262127 Review.
Cited by
-
ARF1.GTP, tyrosine-based signals, and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate constitute a minimal machinery to recruit the AP-1 clathrin adaptor to membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Oct;13(10):3672-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0309. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12388765 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 dependent clathrin-coat assembly on synthetic liposomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Apr 27;96(9):5013-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.9.5013. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10220410 Free PMC article.
-
A GBF1-Dependent Mechanism for Environmentally Responsive Regulation of ER-Golgi Transport.Dev Cell. 2019 Jun 3;49(5):786-801.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 May 2. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 31056345 Free PMC article.
-
Mint3/X11gamma is an ADP-ribosylation factor-dependent adaptor that regulates the traffic of the Alzheimer's Precursor protein from the trans-Golgi network.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jan;19(1):51-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0465. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 17959829 Free PMC article.
-
The Arf family G protein Arl1 is required for secretory granule biogenesis in Drosophila.J Cell Sci. 2014 May 15;127(Pt 10):2151-60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.122028. Epub 2014 Mar 7. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24610947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balch WE, Dunphy WG, Braell WA, Rothman JE. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984;39:405–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

