Gene knockouts reveal separate functions for two cytoplasmic dyneins in Tetrahymena thermophila
- PMID: 10069817
- PMCID: PMC25201
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.771
Gene knockouts reveal separate functions for two cytoplasmic dyneins in Tetrahymena thermophila
Abstract
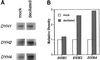
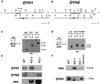
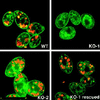
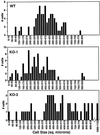
In many organisms, there are multiple isoforms of cytoplasmic dynein heavy chains, and division of labor among the isoforms would provide a mechanism to regulate dynein function. The targeted disruption of somatic genes in Tetrahymena thermophila presents the opportunity to determine the contributions of individual dynein isoforms in a single cell that expresses multiple dynein heavy chain genes. Substantial portions of two Tetrahymena cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain genes were cloned, and their motor domains were sequenced. Tetrahymena DYH1 encodes the ubiquitous cytoplasmic dynein Dyh1, and DYH2 encodes a second cytoplasmic dynein isoform, Dyh2. The disruption of DYH1, but not DYH2, resulted in cells with two detectable defects: 1) phagocytic activity was inhibited, and 2) the cells failed to distribute their chromosomes correctly during micronuclear mitosis. In contrast, the disruption of DYH2 resulted in a loss of regulation of cell size and cell shape and in the apparent inability of the cells to repair their cortical cytoskeletons. We conclude that the two dyneins perform separate tasks in Tetrahymena.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dynein-2 affects the regulation of ciliary length but is not required for ciliogenesis in Tetrahymena thermophila.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(2):708-20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-07-0746. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19019986 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty-five dyneins in Tetrahymena: A re-examination of the multidynein hypothesis.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008 Apr;65(4):342-51. doi: 10.1002/cm.20264. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008. PMID: 18300275
-
Dynein light chain family in Tetrahymena thermophila.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007 Feb;64(2):82-96. doi: 10.1002/cm.20165. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007. PMID: 17009324
-
The dynein heavy chain family.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2004 Jan-Feb;51(1):23-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2004.tb00157.x. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15068262 Review.
-
Evaluating the dynein heavy chain gene family in Tetrahymena.Methods Mol Biol. 2001;161:17-27. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-051-9:017. Methods Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11190505 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
FAP206 is a microtubule-docking adapter for ciliary radial spoke 2 and dynein c.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Feb 15;26(4):696-710. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1506. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25540426 Free PMC article.
-
RAD51 is required for propagation of the germinal nucleus in Tetrahymena thermophila.Genetics. 2000 Apr;154(4):1587-96. doi: 10.1093/genetics/154.4.1587. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10747055 Free PMC article.
-
Dynein-2 affects the regulation of ciliary length but is not required for ciliogenesis in Tetrahymena thermophila.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(2):708-20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-07-0746. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19019986 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and innovation in Tetrahymena membrane traffic: proteins, lipids, and compartments.Methods Cell Biol. 2012;109:141-75. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385967-9.00006-2. Methods Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22444145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis of the model protozoan, Tetrahymena thermophila, using Deep RNA sequencing.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030630. Epub 2012 Feb 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asai DJ. Functional and molecular diversity of dynein heavy chains. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1996;7:311–320.
-
- Asai DJ, Brokaw CJ. Dynein heavy chain isoforms and axonemal motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1993;3:398–402. - PubMed
-
- Asai DJ, Brokaw CJ, Harmon RC, Wilson L. Monoclonal antibodies to tubulin and their effects on the movement of reactivated sea urchin spermatozoa. Cell Motil. 1982;1:175–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

