Mos positively regulates Xe-Wee1 to lengthen the first mitotic cell cycle of Xenopus
- PMID: 10072389
- PMCID: PMC316506
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.5.620
Mos positively regulates Xe-Wee1 to lengthen the first mitotic cell cycle of Xenopus
Abstract
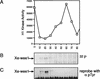
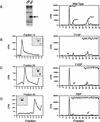
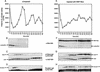
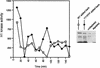
Several key developmental events occur in the first mitotic cell cycle of Xenopus; consequently this cycle has two gap phases and is approximately 60-75 min in length. In contrast, embryonic cycles 2-12 consist only of S and M phases and are 30 min in length. Xe-Wee1 and Mos are translated and degraded in a developmentally regulated manner. Significantly, both proteins are present in the first cell cycle. We showed previously that the expression of nondegradable Mos, during early interphase, delays the onset of M phase in the early embryonic cell cycles. Here we report that Xe-Wee1 is required for the Mos-mediated M-phase delay. We find that Xe-Wee1 tyrosine autophosphorylation positively regulates Xe-Wee1 and is only detected in the first 30 min of the first cell cycle. The level and duration of Xe-Wee1 tyrosine phosphorylation is elevated significantly when the first cell cycle is elongated with nondegradable Mos. Importantly, we show that the tyrosine phosphorylation of Xe-Wee1 is required for the Mos-mediated M-phase delay. These findings indicate that Mos positively regulates Xe-Wee1 to generate the G2 phase in the first cell cycle and establish a direct link between the MAPK signal transduction pathway and Wee1 in vertebrates.
Figures



References
-
- Abrieu A, Lorca T, Labbe J-C, Morin N, Keyse S, Doree M. MAP kinase does not inactivate, but rather prevents the cyclin degradation pathway from being turned on in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Aligue R, Wu L, Russell P. Regulation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Wee1 tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13320–13325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
