The polar flagellar motor of Vibrio cholerae is driven by an Na+ motive force
- PMID: 10074090
- PMCID: PMC93596
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.6.1927-1930.1999
The polar flagellar motor of Vibrio cholerae is driven by an Na+ motive force
Abstract
Vibrio cholerae is a highly motile bacterium which possesses a single polar flagellum as a locomotion organelle. Motility is thought to be an important factor for the virulence of V. cholerae. The genome sequencing project of this organism is in progress, and the genes that are highly homologous to the essential genes of the Na+-driven polar flagellar motor of Vibrio alginolyticus were found in the genome database of V. cholerae. The energy source of its flagellar motor was investigated. We examined the Na+ dependence and the sensitivity to the Na+ motor-specific inhibitor of the motility of the V. cholerae strains and present the evidence that the polar flagellar motor of V. cholerae is driven by an Na+ motive force.
Figures
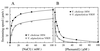
References
-
- Atsumi T, McCarter L, Imae Y. Polar and lateral flagellar motors of marine Vibrio are driven by different ion-motive forces. Nature. 1992;355:182–184. - PubMed
-
- Bakeeva L E, Chumakov K M, Drachev A L, Metlina A L, Skulachev V P. The sodium cycle. III. Vibrio alginolyticus resembles Vibrio cholerae and some other vibriones by flagellar motor and ribosomal 5S-RNA structures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;850:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

