EBP2, a human protein that interacts with sequences of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 important for plasmid maintenance
- PMID: 10074103
- PMCID: PMC104013
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.2587-2595.1999
EBP2, a human protein that interacts with sequences of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 important for plasmid maintenance
Abstract
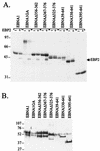
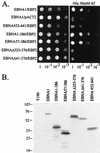
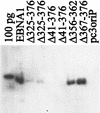
The replication and stable maintenance of latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA episomes in human cells requires only one viral protein, Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1). To gain insight into the mechanisms by which EBNA1 functions, we used a yeast two-hybrid screen to detect human proteins that interact with EBNA1. We describe here the isolation of a protein, EBP2 (EBNA1 binding protein 2), that specifically interacts with EBNA1. EBP2 was also shown to bind to DNA-bound EBNA1 in a one-hybrid system, and the EBP2-EBNA1 interaction was confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation from insect cells expressing these two proteins. EBP2 is a 35-kDa protein that is conserved in a variety of organisms and is predicted to form coiled-coil interactions. We have mapped the region of EBNA1 that binds EBP2 and generated internal deletion mutants of EBNA1 that are deficient in EBP2 interactions. Functional analyses of these EBNA1 mutants show that the ability to bind EBP2 correlates with the ability of EBNA1 to support the long-term maintenance in human cells of a plasmid containing the EBV origin, oriP. An EBNA1 mutant lacking amino acids 325 to 376 was defective for EBP2 binding and long-term oriP plasmid maintenance but supported the transient replication of oriP plasmids at wild-type levels. Thus, our results suggest that the EBNA1-EBP2 interaction is important for the stable segregation of EBV episomes during cell division but not for the replication of the episomes.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Reconstitution of Epstein-Barr virus-based plasmid partitioning in budding yeast.EMBO J. 2001 Jan 15;20(1-2):222-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.1.222. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11226172 Free PMC article.
-
The amino terminus of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 contains AT hooks that facilitate the replication and partitioning of latent EBV genomes by tethering them to cellular chromosomes.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(21):11487-505. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.11487-11505.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15479791 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for Cooperative Binding of EBNA1 to the Epstein-Barr Virus Dyad Symmetry Minimal Origin of Replication.J Virol. 2019 Sep 30;93(20):e00487-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00487-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31142669 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA1 and host factors in Epstein-Barr virus latent DNA replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Dec;2(6):733-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.09.005. Epub 2012 Sep 30. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 23031715 Review.
-
Replication licensing of the EBV oriP minichromosome.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;258:13-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56515-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11443858 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between basic residues of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein and cellular chromatin mediates viral plasmid maintenance.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 16;288(33):24189-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491167. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23836915 Free PMC article.
-
EBP2, a novel NPM-ALK-interacting protein in the nucleolus, contributes to the proliferation of ALCL cells by regulating tumor suppressor p53.Mol Oncol. 2021 Jan;15(1):167-194. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12822. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Mol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33040459 Free PMC article.
-
Sneaking Out for Happy Hour: Yeast-Based Approaches to Explore and Modulate Immune Response and Immune Evasion.Genes (Basel). 2019 Aug 31;10(9):667. doi: 10.3390/genes10090667. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oriP-based episomes requires EBV-encoded nuclear antigen-1 chromosome-binding domains, which can be replaced by high-mobility group-I or histone H1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1865-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1865. Epub 2001 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11172042 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere repeat binding factors TRF1, TRF2, and hRAP1 modulate replication of Epstein-Barr virus OriP.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(22):11992-2001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.11992-12001.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14581536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol. 1. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons; 1991.
-
- Blake N, Lee S, Redchenko I, Thomas W, Steven N, Leese A, Steigerwald-Mullen P, Kurilla M G, Frappier L, Rickinson A. Human CD8+ T cell responses to EBV EBNA1: HLA class I presentation of the (GLY-ALA) containing protein requires exogenous processing. Immunity. 1997;7:791–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

