Charged-to-alanine scanning mutagenesis of the N-terminal half of adeno-associated virus type 2 Rep78 protein
- PMID: 10074114
- PMCID: PMC104024
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.2682-2693.1999
Charged-to-alanine scanning mutagenesis of the N-terminal half of adeno-associated virus type 2 Rep78 protein
Abstract
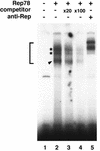
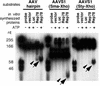
The adeno-associated virus (AAV) Rep78 and Rep68 proteins are required for site-specific integration of the AAV genome into the AAVS1 locus (19q13.3-qter) as well as for viral DNA replication. Rep78 and Rep68 bind to the GAGC motif on the inverted terminal repeat (ITR) and cut at the trs (terminal resolution site). A similar reaction is believed to occur in AAVS1 harboring an analogous GAGC motif and a trs homolog, followed by integration of the AAV genome. To elucidate the functional domains of Rep proteins at the amino acid level, we performed charged-to-alanine scanning mutagenesis of the N terminus (residues 1 to 240) of Rep78, where DNA binding and nicking domains are thought to exist. Mutants were analyzed for their abilities to bind the GAGC motif, nick at the trs homolog, and integrate an ITR-containing plasmid into AAVS1 by electrophoretic mobility shift assay, trs endonuclease assay, and PCR-based integration assay. We identified the residues responsible for DNA binding: R107A, K136A, and R138A mutations completely abolished the binding activity. The H90A or H92A mutant, carrying a mutation in a putative metal binding site, lost nicking activity while retaining binding activity. Mutations affecting DNA binding or trs nicking also impaired the site-specific integration, except for E66A and E239A. These results provide important information on the structure-function relationship of Rep proteins. We also describe an aberrant nicking of Rep78. We found that Rep78 cuts predominantly at the trs homolog not only between the T residues (GGT/TGG), but also between the G and T residues (GG/TTGG), which may be influenced by the sequence surrounding the GAGC motif.
Figures


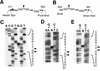


Similar articles
-
Selective cleavage of AAVS1 substrates by the adeno-associated virus type 2 rep68 protein is dependent on topological and sequence constraints.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(19):8831-42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.19.8831-8842.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10982325 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of wild-type and mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) Rep proteins on AAV hairpin DNA.J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2440-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.4.2440-2448.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8642672 Free PMC article.
-
Charge-to-alanine mutagenesis of the adeno-associated virus type 2 Rep78/68 proteins yields temperature-sensitive and magnesium-dependent variants.J Virol. 1999 Nov;73(11):9433-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.11.9433-9445.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10516052 Free PMC article.
-
A Rep recognition sequence is necessary but not sufficient for nicking of DNA by adeno-associated virus type-2 Rep proteins.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 May 15;389(2):271-7. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2348. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11339817
-
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) site-specific recombination does not require a Rep-dependent origin of replication within the AAV terminal repeat.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Nov 20;98(24):13525-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241508998. Epub 2001 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11707592 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Applications of Deep Mutational Scanning in Virology.Viruses. 2021 May 28;13(6):1020. doi: 10.3390/v13061020. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34071591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The putative metal coordination motif in the endonuclease domain of human Parvovirus B19 NS1 is critical for NS1 induced S phase arrest and DNA damage.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(1):79-92. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.8.79. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Int J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22211107 Free PMC article.
-
An adeno-associated virus (AAV) initiator protein, Rep78, catalyzes the cleavage and ligation of single-stranded AAV ori DNA.J Virol. 2000 Apr;74(7):3122-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.7.3122-3129.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10708427 Free PMC article.
-
Amino-terminal domain exchange redirects origin-specific interactions of adeno-associated virus rep78 in vitro.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(7):3230-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.7.3230-3239.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11238849 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Mutant AAV2 Rep Proteins Support AAV2 Replication without Blocking HSV-1 Helpervirus Replication.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170908. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold F H, Haymore B L. Engineered metal-binding proteins: purification to protein folding. Science. 1991;252:1796–1797. - PubMed
-
- Baas P D, Jansz H S. Single-stranded DNA phage origins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;136:31–70. - PubMed
-
- Batchu R B, Hermonat P L. Dissociation of conventional DNA binding and endonuclease activities by an adeno-associated virus Rep78 mutant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;210:717–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

