Silencing of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 gene by the Max-Mad1-mSin3A modulator of chromatin structure
- PMID: 10074148
- PMCID: PMC104058
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.2983-2993.1999
Silencing of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 gene by the Max-Mad1-mSin3A modulator of chromatin structure
Abstract
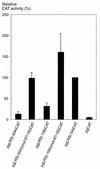
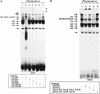
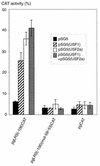
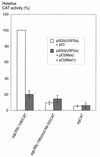
The tumor-associated latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) gene in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome is activated by EBV-encoded proteins and cellular factors that are part of general signal transduction pathways. As previously demonstrated, the proximal region of the LMP1 promoter regulatory sequence (LRS) contains a negative cis element with a major role in EBNA2-mediated regulation of LMP1 gene expression in B cells. Here, we show that this silencing activity overlaps with a transcriptional enhancer in an LRS sequence that contains an E-box-homologous motif. Mutation of the putative repressor binding site relieved the repression both in a promoter-proximal context and in a complete LRS context, indicating a functional role of the repressor. Gel retardation assays showed that members of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family, including Max, Mad1, USF, E12, and E47, and the corepressor mSin3A bound to the E-box-containing sequence. The enhancer activity correlated with the binding of USF. Moreover, the activity of the LMP1 promoter in reporter constructs was upregulated by overexpression of USF1 and USF2a, and the transactivation was inhibited by the concurrent expression of Max and Mad1. This suggests that Max-Mad1-mediated anchorage of a multiprotein complex including mSin3A and histone deacetylases to the E-box site constitutes the basis for the repression. Removal of acetyl moieties from histones H3 and H4 should result in a chromatin structure that is inaccessible to transcription factors. Accordingly, inhibition of deacetylase activity with trichostatin A induced expression of the endogenous LMP1 gene in EBV-transformed cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Role of a consensus AP-2 regulatory sequence within the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 promoter in EBNA2 mediated transactivation.Virus Genes. 2007 Oct;35(2):203-14. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0116-x. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Virus Genes. 2007. PMID: 17546492
-
PU box-binding transcription factors and a POU domain protein cooperate in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2-induced transactivation of the EBV latent membrane protein 1 promoter.J Gen Virol. 1995 Nov;76 ( Pt 11):2679-92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-11-2679. J Gen Virol. 1995. PMID: 7595375
-
Activity of the LMP1 gene promoter in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines is modulated by sequence variations in the promoter-proximal CRE site.J Gen Virol. 2007 Jul;88(Pt 7):1887-1894. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82771-0. J Gen Virol. 2007. PMID: 17554019
-
Mad proteins contain a dominant transcription repression domain.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):5772-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.10.5772. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8816491 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of LMP1 expression by histone deacetylase inhibitors in an EBV carrying NPC cell line.Virus Genes. 2004 Jan;28(1):121-8. doi: 10.1023/B:VIRU.0000012268.35297.ff. Virus Genes. 2004. PMID: 14739656
-
Autoactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus oncogenic protein LMP1 during type II latency through opposite roles of the NF-kappaB and JNK signaling pathways.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7382-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02052-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840319 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 by a lytic transactivator Rta.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(23):13028-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.13028-13036.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15542654 Free PMC article.
-
A positive autoregulatory loop of LMP1 expression and STAT activation in epithelial cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4139-48. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4139-4148.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634372 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a consensus AP-2 regulatory sequence within the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 promoter in EBNA2 mediated transactivation.Virus Genes. 2007 Oct;35(2):203-14. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0116-x. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Virus Genes. 2007. PMID: 17546492
References
-
- Allday M J, Crawford D H, Thomas J A. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Amati B, Land H. Myc-Max-Mad: a transcriptional factor network controlling cell cycle progression, differentiation and death. Curr Biol. 1994;4:102–108. - PubMed
-
- Ayer D E, Kretzner L, Eisenman R N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993;72:211–222. - PubMed
-
- Ayer D E, Lawrence Q A, Eisenman R N. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell. 1995;80:767–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

