A herpesvirus ribosome-associated, RNA-binding protein confers a growth advantage upon mutants deficient in a GADD34-related function
- PMID: 10074192
- PMCID: PMC104102
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.4.3375-3385.1999
A herpesvirus ribosome-associated, RNA-binding protein confers a growth advantage upon mutants deficient in a GADD34-related function
Abstract
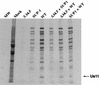
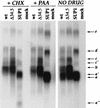
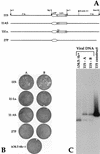
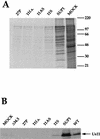
The herpes simplex virus type 1 gamma34.5 gene product and the cellular GADD34 protein both contain similar domains that can regulate the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2), a critical translation initiation factor. Viral mutants that lack the GADD34-related function grow poorly on a variety of malignant human cells, as activation of the cellular PKR kinase leads to the accumulation of inactive, phosphorylated eIF2 at late times postinfection. Termination of translation prior to the completion of the viral reproductive cycle leads to impaired growth. Extragenic suppressors that regain the ability to synthesize proteins efficiently in the absence of the viral GADD34-related function have been isolated. These suppressor alleles are dominant in trans and affect the steady-state accumulation of several viral mRNA species. We demonstrate that deregulated expression of Us11, a virus-encoded RNA-binding, ribosome-associated protein is necessary and sufficient to confer a growth advantage upon viral mutants that lack a GADD34-related function. Ectopic expression of Us11 reduces the accumulation of the activated cellular PKR kinase and allows for sustained protein synthesis. Thus, an RNA-binding, ribosome-associated protein (Us11) and a GADD34-related protein (gamma34.5) both function in a signal pathway that regulates translation by modulating eIF2 phosphorylation.
Figures



References
-
- Brown S M, Harland J. Three mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: one lacking the genes US10, US11, and US12 and two in which Rs has been extended by 6 Kb to 0.91 map units with loss of Us sequences between 0.94 and the Us/TRs junction. J Gen Virol. 1987;68:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Chou J, Kern E R, Whitley R J, Roizman B. Mapping of herpes simplex virus 1 neurovirulence to γ34.5, a gene nonessential for growth in cell culture. Science. 1990;252:1262–1266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

