Modulation of apoptosis by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1)
- PMID: 10074476
- PMCID: PMC408127
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5461
Modulation of apoptosis by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1)
Abstract
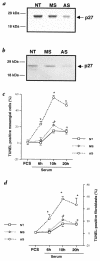
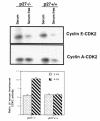
Proliferation and apoptosis are increased in many types of inflammatory diseases. A role for the cyclin kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) (p27) in limiting proliferation has been shown. In this study, we show that p27(-/-) mesangial cells and fibroblasts have strikingly elevated rates of apoptosis, not proliferation, when deprived of growth factors. Apoptosis was rescued by restoration of p27 expression. Cyclin A-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) activity, but not cyclin E-CDK2 activity, was increased in serum-starved p27(-/-) cells, and decreasing CDK2 activity, either pharmacologically (Roscovitine) or by a dominant-negative mutant, inhibited apoptosis. Our results show that a new biological function for the CDK inhibitor p27 is protection of cells from apoptosis by constraining CDK2 activity. These results suggest that CDK inhibitors are necessary for coordinating the cell cycle and cell-death programs so that cell viability is maintained during exit from the cell cycle.
Figures






References
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1149–1163. - PubMed
-
- Zabludoff S, Csete M, Wagner R, Yu X, Wold BJ. p27Kip1 is expressed transiently in developing myotomes and enhances myogenesis. Cell Growth Differ. 1998;9:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Nourse J, et al. Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature. 1994;372:570–573. - PubMed
-
- Polyak K, et al. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994;78:59–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

