Impaired physiological responses to chronic hypoxia in mice partially deficient for hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha
- PMID: 10074486
- PMCID: PMC408131
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5912
Impaired physiological responses to chronic hypoxia in mice partially deficient for hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha
Abstract
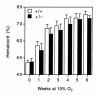
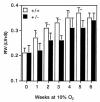
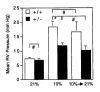
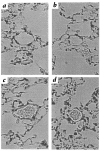
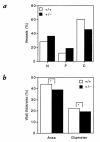
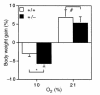
Chronic hypoxia induces polycythemia, pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and weight loss. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) activates transcription of genes encoding proteins that mediate adaptive responses to hypoxia, including erythropoietin, vascular endothelial growth factor, and glycolytic enzymes. Expression of the HIF-1alpha subunit increases exponentially as O2 concentration is decreased. Hif1a-/- mouse embryos with complete deficiency of HIF-1alpha due to homozygosity for a null allele at the Hif1a locus die at midgestation, with multiple cardiovascular malformations and mesenchymal cell death. Hif1a+/- heterozygotes develop normally and are indistinguishable from Hif1a+/+ wild-type littermates when maintained under normoxic conditions. In this study, the physiological responses of Hif1a+/- and Hif1a+/+ mice exposed to 10% O2 for one to six weeks were analyzed. Hif1a+/- mice demonstrated significantly delayed development of polycythemia, right ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary hypertension, and pulmonary vascular remodeling and significantly greater weight loss compared with wild-type littermates. These results indicate that partial HIF-1alpha deficiency has significant effects on multiple systemic responses to chronic hypoxia.
Figures

References
-
- Hultgren HN, Grover RF. Circulatory adaptation to high altitude. Annu Rev Med. 1968;19:119–152. - PubMed
-
- Naeije R. Pulmonary circulation at high altitude. Respiration. 1997;64:429–434. - PubMed
-
- DiCarlo VS, et al. ETA-receptor antagonism prevents and reverses chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in rat. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:L690–L697. - PubMed
-
- Hales CA, Kradin RL, Brandstetter RD, Zhu Y-J. Impairment of hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by heparin in mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983;128:747–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

