Isolation of a human rotavirus strain with a super-short RNA pattern and a new P2 subtype
- PMID: 10074557
- PMCID: PMC88680
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.4.1213-1216.1999
Isolation of a human rotavirus strain with a super-short RNA pattern and a new P2 subtype
Abstract
Super-short rotavirus strains that have a rearranged gene segment 11 are rarely found in humans, and only five isolates, all from Southeast Asia, have been described in the literature. We report the first isolation in Japan from an infant with severe diarrhea of a rotavirus possessing a super-short RNA pattern. This strain, designated AU19, had a G1 VP7 and is also the first isolate in Japan that possesses a P2[6] VP4. Furthermore, the P2[6] VP4 carried by AU19 was divergent in the hypervariable region of the amino acid sequence from the P2A[6] VP4s carried by asymptomatic neonatal strains or from the P2B[6] VP4 carried by porcine rotavirus strain Gottfried. Thus, AU19 is likely to represent a new VP4 subtype, which we propose to call P2C. Given the recent emergence of the P2[6] VP4s in India, Brazil, and the United States and the role of VP4 in protective immunity, further scrutiny is justified to see whether the emergence of the previously underrepresented P2[6] VP4 serotype is related to this new P2 subtype.
Figures
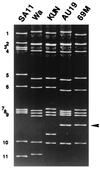
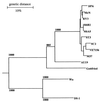
References
-
- Estes M K. Rotaviruses and their replication. In: Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, editors. Fields virology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1996. pp. 1625–1655.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

