The cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk2 regulates thymocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 10075979
- PMCID: PMC2193040
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.6.957
The cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk2 regulates thymocyte apoptosis
Abstract
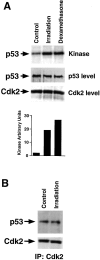
Aberrant activation of cell cycle molecules has been postulated to play a role in apoptosis ("catastrophic cell cycle"). Here we show that in noncycling developing thymocytes, the cyclin- dependent kinase Cdk2 is activated in response to all specific and nonspecific apoptotic stimuli tested, including peptide-specific thymocyte apoptosis. Cdk2 was found to function upstream of the tumor suppressor p53, transactivation of the death promoter Bax, alterations of mitochondrial permeability, Bcl-2, caspase activation, and caspase-dependent proteolytic cleavage of the retinoblastoma protein. Inhibition of Cdk2 completely protected thymocytes from apoptosis, mitochondrial changes, and caspase activation. These data provide the first evidence that Cdk2 activity is crucial for the induction of thymocyte apoptosis.
Figures









References
-
- White E. Death-defying acts: a meeting review on apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993;7:2277–2284. - PubMed
-
- Green DR, Scott DW. Activation-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994;6:476–487. - PubMed
-
- King LB, Ashwell JD. Signaling for death of lymphoid cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993;5:368–373. - PubMed
-
- Martin JS, Green RD. Protease activation during apoptosis: death by thousand cuts? . Cell. 1995;82:349–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

