The insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-dependent IGF binding protein-4 protease secreted by human fibroblasts is pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A
- PMID: 10077652
- PMCID: PMC15910
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.3149
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-dependent IGF binding protein-4 protease secreted by human fibroblasts is pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A
Abstract
Proteolytic cleavage of the six known insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) is a powerful means of rapid structure and function modification of these important growth-regulatory proteins. Intact IGFBP-4 is a potent inhibitor of IGF action in vitro, and cleavage of IGFBP-4 has been shown to abolish its ability to inhibit IGF stimulatory effects in a variety of systems, suggesting that IGFBP-4 proteolysis acts as a positive regulator of IGF bioavailability. Here we report the isolation of an IGF-dependent IGFBP-4-specific protease from human fibroblast-conditioned media and its identification by mass spectrometry microsequencing as pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A), a protein of unknown function found in high concentrations in the maternal circulation during pregnancy. Antibodies raised against PAPP-A both inhibited and immunodepleted IGFBP-4 protease activity in human fibroblast-conditioned media. Moreover, PAPP-A purified from pregnancy sera had IGF-dependent IGFBP-4 protease activity. PAPP-A mRNA was expressed by the human fibroblasts and osteoblasts, and PAPP-A protein was secreted into the culture medium. In conclusion, we have identified an IGF-dependent IGFBP protease and at the same time assigned a function to PAPP-A. This represents an unanticipated union of two areas of research that were not linked in any way before this report.
Figures


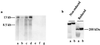
References
-
- Daughaday W H, Rotwein P. Endocr Rev. 1989;10:68–90. - PubMed
-
- D’Ercole A J. Growth Dis. 1996;25:573–590. - PubMed
-
- Shimisaki S, Ling N. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3:243–266. - PubMed
-
- Jones J I, Clemmons D R. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:3–34. - PubMed
-
- Fowlkes J L. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997;8:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

