A functional granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor is required for normal chemoattractant-induced neutrophil activation
- PMID: 10079103
- PMCID: PMC408143
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5191
A functional granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor is required for normal chemoattractant-induced neutrophil activation
Abstract
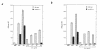
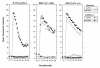
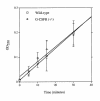
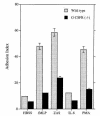
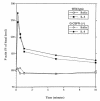
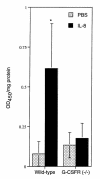
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a hematopoietic growth factor that is widely used to treat neutropenia. In addition to stimulating polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) production, G-CSF may have significant effects on PMN function. Because G-CSF receptor (G-CSFR)-deficient mice do not have the expected neutrophilia after administration of human interleukin-8 (IL-8), we examined the effect of the loss of G-CSFR on IL-8-stimulated PMN function. Compared with wild-type PMNs, PMNs isolated from G-CSFR-deficient mice demonstrated markedly decreased chemotaxis to IL-8. PMN emigration into the skin of G-CSFR-deficient mice in response to IL-8 was also impaired. Significant chemotaxis defects were also seen in response to N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, zymosan-activated serum, or macrophage inflammatory protein-2. The defective chemotactic response to IL-8 does not appear to be due to impaired chemoattractant receptor function, as the number of IL-8 receptors and chemoattractant-induced calcium influx, actin polymerization, and release of gelatinase B were comparable to those of wild-type PMNs. Chemoattractant-induced adhesion of G-CSFR-deficient PMNs was significantly impaired, suggesting a defect in beta2-integrin activation. Collectively, these data demonstrate that selective defects in PMN activation are present in G-CSFR-deficient mice and indicate that G-CSF plays an important role in regulating PMN chemokine responsiveness.
Figures

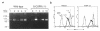
Similar articles
-
Chemoattractants induce rapid release of the interleukin 1 type II decoy receptor in human polymorphonuclear cells.J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2181-6. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2181. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7760005 Free PMC article.
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor potentiates human polymorphonuclear leukocyte aggregation responses to formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine.Immunol Lett. 1992 Mar;32(1):71-9. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(92)90202-y. Immunol Lett. 1992. PMID: 1323527
-
Regulation of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor and Its Receptor in Skeletal Muscle is Dependent Upon the Type of Inflammatory Stimulus.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):710-9. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0159. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 26057332
-
Neutrophil gelatinase B and chemokines in leukocytosis and stem cell mobilization.Leuk Lymphoma. 2002 Feb;43(2):233-41. doi: 10.1080/10428190290005982. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. PMID: 11999552 Review.
-
Role of interleukin-8 in neutrophil signaling.Curr Opin Hematol. 2000 May;7(3):178-82. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200005000-00009. Curr Opin Hematol. 2000. PMID: 10786656 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of myeloid-specific integrin alpha Mbeta 2 (CD11b/CD18) expression by cytokines is regulated by Stat3-dependent activation of PU.1.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 24;277(21):19001-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112271200. Epub 2002 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11889125 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Reduces Neutrophil Responses Favoring Bacterial Survival.J Innate Immun. 2024;16(1):489-500. doi: 10.1159/000541414. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Innate Immun. 2024. PMID: 39293427 Free PMC article.
-
Gelatinase B is required for alveolar bronchiolization after intratracheal bleomycin.Am J Pathol. 2000 Aug;157(2):525-35. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64563-4. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10934155 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of systemic and local neutrophil responses by G-CSF during pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.Blood. 2007 Apr 15;109(8):3235-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-015081. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17185469 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous glucocorticoids modulate neutrophil function in a murine model of haemolytic uraemic syndrome.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Jan;139(1):65-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02659.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15606615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsushima K, Oppenheim JJ. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL-1 and TNF. Cytokine. 1989;1:2–13. - PubMed
-
- Hoch RC, Schraufstätter IU, Cochrane CG. In vivo, in vitro, and molecular aspects of interleukin-8 and the interleukin-8 receptors. J Lab Clin Med. 1996;128:134–145. - PubMed
-
- Matsukawa A, et al. Neutrophil accumulation and activation by homologous Il-8 in rabbits. J Immunol. 1995;154:5418–5425. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd AR, et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and lipopolysaccharide regulate the expression of interleukin 8 receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28188–28192. - PubMed
-
- Anderlini P, Przepiorka D, Champlin R, Korbling M. Biologic and clinical effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in normal individuals. Blood. 1996;88:2819–2825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

