Selective activation and functional significance of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated neutrophils
- PMID: 10079106
- PMCID: PMC408145
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5257
Selective activation and functional significance of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated neutrophils
Abstract
Activation of leukocytes by proinflammatory stimuli selectively initiates intracellular signal transduction via sequential phosphorylation of kinases. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation of human neutrophils is known to result in activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPk); however, the upstream activator(s) of p38 MAPk is unknown, and consequences of p38 MAPk activation remain largely undefined. We investigated the MAPk kinase (MKK) that activates p38 MAPk in response to LPS, the p38 MAPk isoforms that are activated as part of this pathway, and the functional responses affected by p38 MAPk activation. Although MKK3, MKK4, and MKK6 all activated p38 MAPk in experimental models, only MKK3 was found to activate recombinant p38 MAPk in LPS-treated neutrophils. Of p38 MAPk isoforms studied, only p38alpha and p38delta were detected in neutrophils. LPS stimulation selectively activated p38alpha. Specific inhibitors of p38alpha MAPk blocked LPS-induced adhesion, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation, and synthesis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Inhibition of p38alpha MAPk resulted in a transient decrease in TNF-alpha mRNA accumulation but persistent loss of TNF-alpha synthesis. These findings support a pathway by which LPS stimulation of neutrophils results in activation of MKK3, which in turn activates p38alpha MAPk, ultimately regulating adhesion, NF-kappaB activation, enhanced gene expression of TNF-alpha, and regulation of TNF-alpha synthesis.
Figures

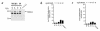

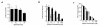
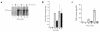


Similar articles
-
Cytokine-specific activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase subtype cascades in human neutrophils stimulated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Blood. 1999 Jan 1;93(1):341-9. Blood. 1999. PMID: 9864179
-
Intracellular signaling in rat cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: roles of nuclear factor-kappaB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase on tumor necrosis factor-alpha production.Endocrinology. 1999 Aug;140(8):3562-72. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.8.6914. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10433212
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades during priming of human neutrophils by TNF-alpha and GM-CSF.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Oct;64(4):537-45. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9766635
-
Nuclear export of the stress-activated protein kinase p38 mediated by its substrate MAPKAP kinase-2.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1049-57. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70442-7. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768359 Review.
-
[The signal transduction of cell activation by LPS: the studies from CD14 to p38 MAPK].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 1999 Jan;30(1):29-34. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 1999. PMID: 12532845 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Proteomic identification of 14-3-3zeta as a mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 substrate: role in dimer formation and ligand binding.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(15):5376-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5376-5387.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12861023 Free PMC article.
-
Redox/ROS regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation and MAPK-mediated TNF-alpha biosynthesis.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(2):520-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704467. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11815388 Free PMC article.
-
DA-9601, a standardized extract of Artemisia asiatica, blocks TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 and CCL20 production by inhibiting p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways in human gastric epithelial cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 14;12(30):4850-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4850. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16937467 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Phytochemically Characterized Extracts From Syringa vulgaris and Isolated Secoiridoids on Mediators of Inflammation in a Human Neutrophil Model.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 11;9:349. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00349. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29695965 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057285. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ. How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:14843–14846. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Lee J-D, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265:808–811. - PubMed
-
- Rouse J, et al. A novel kinase cascade triggered by chemical stress and heat shock which stimulates MAPKAP-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell. 1994;78:1027–1037. - PubMed
-
- Lee JC, et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994;372:739–746. - PubMed
-
- Nick JA, et al. Activation of a p38 MAPk in human neutrophils by LPS. J Immunol. 1996;156:4867–4875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

