Apoptosis in nontumorous and neoplastic human pituitaries: expression of the Bcl-2 family of proteins
- PMID: 10079254
- PMCID: PMC1866431
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65323-0
Apoptosis in nontumorous and neoplastic human pituitaries: expression of the Bcl-2 family of proteins
Abstract
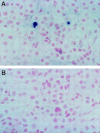
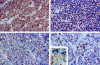
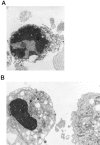
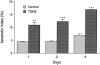
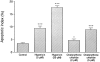
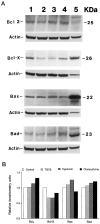
Analyses of apoptosis and of the apoptosis regulatory proteins Bcl-2, Bax, Bcl-X, and Bad were done in 95 nontumorous and neoplastic pituitary tissues by terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL), immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting. The apoptotic index was relatively low in all groups but was at least fourfold higher in pituitary carcinomas compared with any other groups. Pituitaries from pregnant and postpartum women had a fivefold higher apoptotic index compared with matched controls from nonpregnant females. Preoperative treatment of adenomas with octreotide or dopamine agonists did not change the apoptotic index significantly. The lowest levels of Bcl-2, Bax, and Bcl-X expression were in pituitary carcinomas as detected by immunostaining. An immortalized human pituitary adenoma cell line, HP75, developed in our laboratory using a replication-defective recombinant human adenovirus with an early large T-antigen, had a much higher level of apoptosis than nontumorous and neoplastic pituitaries. Treatment with transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 and protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors increased apoptosis in this cell line. Analysis of the Bcl-2 family of proteins after treatment with TGF-beta1 and PKC inhibitors showed a 20% to 30% decrease in Bcl-X in the treated groups compared with controls. These results, which represent the first study of apoptosis in pituitaries from pregnant and postpartum cases and in pituitary carcinomas, indicate that 1) the apoptotic rate is low in nontumorous and neoplastic pituitary tissues but is relatively higher in pituitary carcinomas, 2) there are alterations in the expression of the Bcl-2 family of proteins in pituitary neoplasms with a decrease in Bcl-2 expression in pituitary carcinomas that may contribute to pituitary tumor pathogenesis and/or proliferation, and 3) cultured pituitary tumor cells respond to TGF-beta1 and PKC inhibitors by undergoing apoptotic cell death.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptosis: its role in pituitary development and neoplastic pituitary tissue.Pituitary. 2014 Apr;17(2):157-62. doi: 10.1007/s11102-013-0481-5. Pituitary. 2014. PMID: 23512699 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta, transforming growth factor-beta receptor II, and p27Kip1 expression in nontumorous and neoplastic human pituitaries.Am J Pathol. 1997 Aug;151(2):509-19. Am J Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9250163 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses tumor cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating Bcl-2 protein expression.Pathol Res Pract. 2009;205(12):828-37. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Jul 21. Pathol Res Pract. 2009. PMID: 19625133
-
Pituitary specific transcription factor messenger ribonucleic expression in adenomatous and nontumorous human pituitary tissues.Lab Invest. 1993 Nov;69(5):570-5. Lab Invest. 1993. PMID: 8246449
-
Morphology, molecular regulation and significance of apoptosis in pituitary adenomas.Front Horm Res. 2004;32:217-34. doi: 10.1159/000079047. Front Horm Res. 2004. PMID: 15281349 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis: its role in pituitary development and neoplastic pituitary tissue.Pituitary. 2014 Apr;17(2):157-62. doi: 10.1007/s11102-013-0481-5. Pituitary. 2014. PMID: 23512699 Review.
-
Bcl-2 Gene Family in Endocrine Pathology: A Review.Endocr Pathol. 2000 Autumn;11(3):205-213. doi: 10.1385/ep:11:3:205. Endocr Pathol. 2000. PMID: 12114693
-
Poorly differentiated synovial sarcoma: a case report.Pathol Oncol Res. 2001;7(1):63-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03032608. Pathol Oncol Res. 2001. PMID: 11411458
-
The hallmarks of cancer… in pituitary tumors?Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023 Apr;24(2):177-190. doi: 10.1007/s11154-022-09777-y. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 36586070 Review.
-
MicroRNA profile indicates downregulation of the TGFβ pathway in sporadic non-functioning pituitary adenomas.Pituitary. 2011 Jun;14(2):112-24. doi: 10.1007/s11102-010-0268-x. Pituitary. 2011. PMID: 21063788
References
-
- Schwartzman RA, Cidlowski JA: Apoptosis: the biochemistry and molecular biology of programmed cell death. Endocr Rev 1993, 14:133-151 - PubMed
-
- Thompson EB: Apoptosis and steroid hormones. Mol Endocrinol 1994, 8:665-673 - PubMed
-
- Drewett N, Jacobi JM, Willgoss DA, Lloyd HM: Apoptosis in the anterior pituitary gland of the rat: studies with estrogen and bromocriptine. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 57:89-95 - PubMed
-
- Yin D, Kondo S, Takeuchi J, Morimura T: Induction of apoptosis in murine ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma cells by bromocriptine. FEBS Lett 1994, 339:73-75 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

