Exposure to hyperoxia decreases the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in adult rat lungs
- PMID: 10079260
- PMCID: PMC1866417
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65329-1
Exposure to hyperoxia decreases the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in adult rat lungs
Abstract
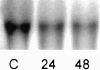
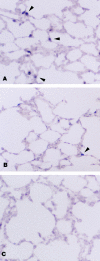
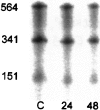
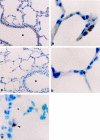
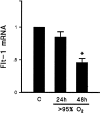
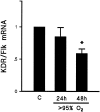
Exposure to high levels of inspired oxygen leads to respiratory failure and death in many animal models. Endothelial cell death is an early finding, before the onset of respiratory failure. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is highly expressed in the lungs of adult animals. In the present study, adult Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to >95% FiO2 for 24 or 48 hours. Northern blot analysis revealed a marked reduction in VEGF mRNA abundance by 24 hours, which decreased to less than 50% of control by 48 hours. In situ hybridization revealed that VEGF was highly expressed in distal airway epithelial cells in controls but disappeared in the oxygen-exposed animals. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analyses demonstrated that VEGF protein was decreased at 48 hours. TUNEL staining demonstrated the presence of apoptotic cells coincident with the decline in VEGF. Abundance of VEGF receptor mRNAs (Flt-1 and KDR/Flk) decreased in the late time points of the study (48 hours), possibly secondary to the loss of endothelial cells. We speculate that VEGF functions as a survival factor in the normal adult rat lung, and its loss during hyperoxia contributes to the pathophysiology of oxygen-induced lung damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of retinal vascular endothelial growth factor and receptors in rabbits exposed to hyperoxia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 May;43(5):1546-57. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 11980873
-
Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor KDR/Flk gene expression through adenosine A2 receptors in retinal capillary endothelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996 Jun;37(7):1311-21. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996. PMID: 8641834
-
Differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor fms-like-tyrosine kinase is mediated by nitric oxide in rat renal mesangial cells.Biochem J. 1999 Mar 1;338 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):367-74. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10024512 Free PMC article.
-
The splice variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors.J Cell Sci. 2001 Mar;114(Pt 5):853-65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.5.853. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11181169 Review.
-
Endothelial receptor tyrosine kinases involved in blood vessel development and tumor angiogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;476:57-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4221-6_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10949655 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) as a novel inhibitor of tubulogenesis: RGS4 inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinases and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):609-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0479. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15548600 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal hyperoxia exposure differentially affects hepatocytes and liver haemopoietic cells in newborn rats.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 12;9(8):e105005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105005. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25115881 Free PMC article.
-
Umbilical cord blood exosomes from very preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia aggravate lung injury in mice.Sci Rep. 2023 May 27;13(1):8648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35620-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37244977 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of pioglitazone, a PPARγ agonist, and synthetic surfactant B-YL prevents hyperoxia-induced lung injury in adult mice lung explants.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Jun;80:102209. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102209. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36907545 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of trauma, hemorrhagic shock, and chronic stress on lung vascular endothelial growth factor.J Surg Res. 2017 Apr;210:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.10.023. Epub 2016 Nov 2. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28457321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crapo JD, Barry BE, Foscue HA, Shelburne J: Structural and biochemical changes in rat lungs occurring during exposures to lethal and adaptive doses of oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis 1980, 122:123-143 - PubMed
-
- Royston BD, Webster NR, Nunn JF: Time course of changes in lung permeability and edema in the rat exposed to 100% oxygen. J Appl Physiol 1990, 69:1532-1537 - PubMed
-
- Bryan CL, Jenkinson SG: Oxygen toxicity. Clin Chest Med 1988, 9:141-152 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

