Double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase PKR enhances transcriptional activation by tumor suppressor p53
- PMID: 10082513
- PMCID: PMC84040
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.4.2475
Double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase PKR enhances transcriptional activation by tumor suppressor p53
Abstract
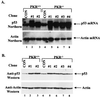
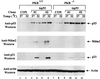
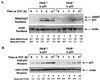
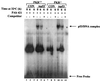
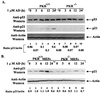
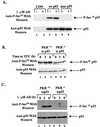
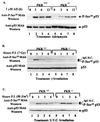
The tumor suppressor p53 plays a key role in inducing G1 arrest and apoptosis following DNA damage. The double-stranded-RNA-activated protein PKR is a serine/threonine interferon (IFN)-inducible kinase which plays an important role in regulation of gene expression at both transcriptional and translational levels. Since a cross talk between IFN-inducible proteins and p53 had already been established, we investigated whether and how p53 function was modulated by PKR. We analyzed p53 function in several cell lines derived from PKR+/+ and PKR-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) after transfection with the temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant of mouse p53 [p53(Val135)]. Here we report that transactivation of transcription by p53 and G0/G1 arrest were impaired in PKR-/- cells upon conditions that ts p53 acquired a wild-type conformation. Phosphorylation of mouse p53 on Ser18 was defective in PKR-/- cells, consistent with an impaired transcriptional induction of the p53-inducible genes encoding p21(WAF/Cip1) and Mdm2. In addition, Ser18 phosphorylation and transcriptional activation by mouse p53 were diminished in PKR-/- cells after DNA damage induced by the anticancer drug adriamycin or gamma radiation but not by UV radiation. Furthermore, the specific phosphatidylinositol-3 (PI-3) kinase inhibitor LY294002 inhibited the induction of phosphorylation of Ser18 of p53 by adriamycin to a higher degree in PKR+/+ cells than in PKR-/- cells. These novel findings suggest that PKR enhances p53 transcriptional function and implicate PKR in cell signaling elicited by a specific type of DNA damage that leads to p53 phosphorylation, possibly through a PI-3 kinase pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham N, Stojdl D F, Duncan P I, Methot N, Ishii T, Dube M, Vanderhyden B C, Atkins H L, Gray D A, McBurney M W, Koromilas A E, Brown E G, Sonenberg N, Bell J C. Characterization of transgenic mice with targeted disruption of the catalytic domain of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5953–5962. - PubMed
-
- Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S-Y, Taya Y, Anderson C W, Chessa L, Smorodinsky I, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y, Ziv Y. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science. 1998;281:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Bogue M A, Zhu C, Aguilar-Cordova E, Donehower L A, Roth D B. p53 is required for both radiation-induced differentiation and rescue of V(D)J rearrangement in scid mouse thymocytes. Genes Dev. 1996;10:553–565. - PubMed
-
- Canman C E, Lim D-S, Cimprich K A, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appela E, Kastan M B, Siliciano J D. Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science. 1998;281:1677–1679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
