Maturation of the myogenic program is induced by postmitotic expression of insulin-like growth factor I
- PMID: 10082578
- PMCID: PMC84105
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.4.3115
Maturation of the myogenic program is induced by postmitotic expression of insulin-like growth factor I
Abstract
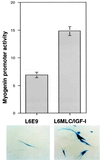
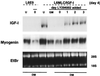
The molecular mechanisms underlying myogenic induction by insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) are distinct from its proliferative effects on myoblasts. To determine the postmitotic role of IGF-I on muscle cell differentiation, we derived L6E9 muscle cell lines carrying a stably transfected rat IGF-I gene under the control of a myosin light chain (MLC) promoter-enhancer cassette. Expression of MLC-IGF-I exclusively in differentiated L6E9 myotubes, which express the embryonic form of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) and no endogenous IGF-I, resulted in pronounced myotube hypertrophy, accompanied by activation of the neonatal MyHC isoform. The hypertrophic myotubes dramatically increased expression of myogenin, muscle creatine kinase, beta-enolase, and IGF binding protein 5 and activated the myocyte enhancer factor 2C gene which is normally silent in this cell line. MLC-IGF-I induction in differentiated L6E9 cells also increased the expression of a transiently transfected LacZ reporter driven by the myogenin promoter, demonstrating activation of the differentiation program at the transcriptional level. Nuclear reorganization, accumulation of skeletal actin protein, and an increased expression of beta1D integrin were also observed. Inhibition of the phosphatidyl inositol (PI) 3-kinase intermediate in IGF-I-mediated signal transduction confirmed that the PI 3-kinase pathway is required only at early stages for IGF-I-mediated hypertrophy and neonatal MyHC induction in these cells. Expression of IGF-I in postmitotic muscle may therefore play an important role in the maturation of the myogenic program.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Permissive roles of phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase and Akt in skeletal myocyte maturation.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Feb;15(2):497-505. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-05-0351. Epub 2003 Oct 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14595115 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factors require phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to signal myogenesis: dominant negative p85 expression blocks differentiation of L6E9 muscle cells.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Jan;12(1):66-77. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.1.0047. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9440811
-
p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases regulate the myogenic program at multiple steps.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jun;20(11):3951-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.11.3951-3964.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10805738 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regeneration: interplay between the myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) pathways.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Nov;70(21):4117-30. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1330-4. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23552962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis.Endocr Rev. 1996 Oct;17(5):481-517. doi: 10.1210/edrv-17-5-481. Endocr Rev. 1996. PMID: 8897022 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia.Aging Cell. 2019 Jun;18(3):e12954. doi: 10.1111/acel.12954. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Aging Cell. 2019. PMID: 30953403 Free PMC article.
-
Postmitotic Expression of SOD1(G93A) Gene Affects the Identity of Myogenic Cells and Inhibits Myoblasts Differentiation.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:537853. doi: 10.1155/2015/537853. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26491230 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I E-peptide activity is dependent on the IGF-I receptor.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045588. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029120 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of IGF-I-calcineurin-NFATc3-dependent pathway genes in skeletal muscle during early development between duck breeds differing in growth rates.Dev Genes Evol. 2015 Jun;225(3):139-48. doi: 10.1007/s00427-015-0501-8. Epub 2015 May 13. Dev Genes Evol. 2015. PMID: 25963597
-
The small muscle-specific protein Csl modifies cell shape and promotes myocyte fusion in an insulin-like growth factor 1-dependent manner.J Cell Biol. 2001 May 28;153(5):985-98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.5.985. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11381084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azzarello G, Sartore S, Saggin L, Gorza L, D’Andrea E, Chieco-Bianchi L, Schiaffino S. Myosin isoform expression in rat rhabdomyosarcoma induced by moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1987;113:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri G, De Angelis L, Feo S, Cossu G, Giallongo A. Differential expression of muscle-specific enolase in embryonic and fetal myogenic cells during mouse development. Differentiation. 1990;45:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis R L, Lockshon D, Turner D L, Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding protein. Cell. 1990;61:49–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
