Chemokine secretion of human cells in response to Toxoplasma gondii infection
- PMID: 10084985
- PMCID: PMC96495
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.4.1547-1552.1999
Chemokine secretion of human cells in response to Toxoplasma gondii infection
Abstract
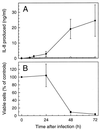
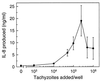
The ubiquitous protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in neonates and immunocompromised hosts. Both acute invasion and reactivation of latent infection result in an inflammatory reaction with lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. The mechanisms responsible for triggering the local host response to toxoplasmosis are not fully understood. Infection of monolayers of human HeLa epithelial cells and fibroblasts with T. gondii resulted in a marked increase in the expression of interleukin-8 (IL-8)-specific mRNA and secretion of the proinflammatory and chemoattractant cytokines interleukin-8 (IL-8), GROalpha, and MCP-1. Host cell invasion and lysis were required for this response, as tachyzoite lysates alone had no effect on IL-8 secretion. IL-8 release was dependent on the release of soluble host cell factors: IL-1alpha in HeLa cells and an additional mediator in fibroblasts. HT-29 epithelial cells, which lack IL-1alpha or another IL-8-inducing activity, did not release IL-8 after infection, although they were efficiently infected with T. gondii and increased IL-8 secretion in response to added IL-1alpha. These data suggest that proinflammatory chemokine secretion is an important host cell response to toxoplasmosis and that the release of IL-1alpha and other mediators from lysed host cells is critical for this chemokine response.
Figures


References
-
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. - PubMed
-
- Bertoli F, Espino M, Arosemena J R, Fishback J L, Frenkel J K. A spectrum in the pathology of toxoplasmosis in patients with AIDS. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995;119:214–224. - PubMed
-
- Carrazana E J, Rossitch E, Samuels M A. Cerebral toxoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1989;91:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Dupey J P, Speer C A, Shen S K, Kwok O C H, Blixt J A. Oocyst-induced murine toxoplasmosis: life cycle, pathogenicity, and stage conversion in mice fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. J Parasitol. 1997;83:870–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

