SNARE membrane trafficking dynamics in vivo
- PMID: 10085287
- PMCID: PMC2148207
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.144.5.869
SNARE membrane trafficking dynamics in vivo
Abstract
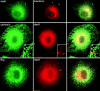
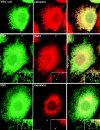
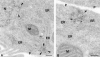
The ER/Golgi soluble NSF attachment protein receptor (SNARE) membrin, rsec22b, and rbet1 are enriched in approximately 1-micrometer cytoplasmic structures that lie very close to the ER. These appear to be ER exit sites since secretory cargo concentrates in and exits from these structures. rsec22b and rbet1 fused to fluorescent proteins are enriched at approximately 1-micrometer ER exit sites that remained more or less stationary, but periodically emitted streaks of fluorescence that traveled generally in the direction of the Golgi complex. These exit sites were reused and subsequent tubules or streams of vesicles followed similar trajectories. Fluorescent membrin- enriched approximately 1-micrometer peripheral structures were more mobile and appeared to translocate through the cytoplasm back and forth, between the periphery and the Golgi area. These mobile structures could serve to collect secretory cargo by fusing with ER-derived vesicles and ferrying the cargo to the Golgi. The post-Golgi SNAREs, syntaxin 6 and syntaxin 13, when fused to fluorescent proteins each displayed characteristic patterns of movement. However, syntaxin 13 was the only SNARE whose life cycle appeared to involve interactions with the plasma membrane. These studies reveal the in vivo spatiotemporal dynamics of SNARE proteins and provide new insight into their roles in membrane trafficking.
Figures

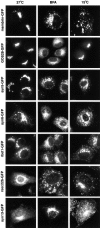


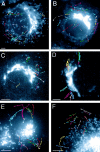
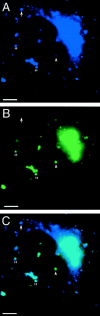
Similar articles
-
Localization, dynamics, and protein interactions reveal distinct roles for ER and Golgi SNAREs.J Cell Biol. 1998 Jun 29;141(7):1489-502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.7.1489. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9647643 Free PMC article.
-
The mammalian protein (rbet1) homologous to yeast Bet1p is primarily associated with the pre-Golgi intermediate compartment and is involved in vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus.J Cell Biol. 1997 Dec 1;139(5):1157-68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.5.1157. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9382863 Free PMC article.
-
Subunit structure of a mammalian ER/Golgi SNARE complex.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39631-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007684200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11035026
-
SNAREs and membrane fusion in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):9-31. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00044-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714710 Review.
-
The plant ER-Golgi interface: a highly structured and dynamic membrane complex.J Exp Bot. 2007;58(1):49-64. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl135. Epub 2006 Sep 21. J Exp Bot. 2007. PMID: 16990376 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct SNARE complexes mediating membrane fusion in Golgi transport based on combinatorial specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 16;99(8):5424-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082100899. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11959998 Free PMC article.
-
STX5 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Adhesion and Promotes Metastasis by Regulating the PI3K/mTOR Pathway.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Jun 28;11(3):572-583. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00276. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36969886 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation and prion transmission study in mice with genetic reduction of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease risk gene Stx6.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Jan;190:106363. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106363. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 37996040 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of tubulovesicular recycling endosomes in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 1999 Dec 1;19(23):10324-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-23-10324.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10575030 Free PMC article.
-
MARCH-II is a syntaxin-6-binding protein involved in endosomal trafficking.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Apr;16(4):1696-710. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-03-0216. Epub 2005 Feb 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15689499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advani RJ, Bae HR, Bock JB, Chao DS, Doung YC, Prekeris R, Yoo JS, Scheller RH. Seven novel mammalian SNARE proteins localize to distinct membrane compartments. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10317–10324. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, McCafferey JM, Plunter H, Farquhar MG. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is sorted and concentrated during export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;76:841–852. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann JE. Using temperature-sensitive mutants of VSV to study membrane protein biogenesis. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:85–110. - PubMed

