Type IIA procollagen containing the cysteine-rich amino propeptide is deposited in the extracellular matrix of prechondrogenic tissue and binds to TGF-beta1 and BMP-2
- PMID: 10085302
- PMCID: PMC2148200
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.144.5.1069
Type IIA procollagen containing the cysteine-rich amino propeptide is deposited in the extracellular matrix of prechondrogenic tissue and binds to TGF-beta1 and BMP-2
Abstract
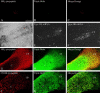
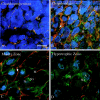
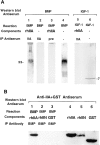
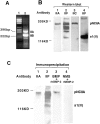
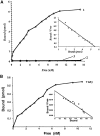
Type II procollagen is expressed as two splice forms. One form, type IIB, is synthesized by chondrocytes and is the major extracellular matrix component of cartilage. The other form, type IIA, contains an additional 69 amino acid cysteine-rich domain in the NH2-propeptide and is synthesized by chondrogenic mesenchyme and perichondrium. We have hypothesized that the additional protein domain of type IIA procollagen plays a role in chondrogenesis. The present study was designed to determine the localization of the type IIA NH2-propeptide and its function during chondrogenesis. Immunofluorescence histochemistry using antibodies to three domains of the type IIA procollagen molecule was used to localize the NH2-propeptide, fibrillar domain, and COOH-propeptides of the type IIA procollagen molecule during chondrogenesis in a developing human long bone (stage XXI). Before chondrogenesis, type IIA procollagen was synthesized by chondroprogenitor cells and deposited in the extracellular matrix. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed type IIA procollagen fibrils labeled with antibodies to NH2-propeptide at approximately 70 nm interval suggesting that the NH2-propeptide remains attached to the collagen molecule in the extracellular matrix. As differentiation proceeds, the cells switch synthesis from type IIA to IIB procollagen, and the newly synthesized type IIB collagen displaces the type IIA procollagen into the interterritorial matrix. To initiate studies on the function of type IIA procollagen, binding was tested between recombinant NH2-propeptide and various growth factors known to be involved in chondrogenesis. A solid phase binding assay showed no reaction with bFGF or IGF-1, however, binding was observed with TGF-beta1 and BMP-2, both known to induce endochondral bone formation. BMP-2, but not IGF-1, coimmunoprecipitated with type IIA NH2-propeptide. Recombinant type IIA NH2-propeptide and type IIA procollagen from media coimmunoprecipitated with BMP-2 while recombinant type IIB NH2-propeptide and all other forms of type II procollagens and mature collagen did not react with BMP-2. Taken together, these results suggest that the NH2-propeptide of type IIA procollagen could function in the extracellular matrix distribution of bone morphogenetic proteins in chondrogenic tissue.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Type IIA procollagen amino propeptide is localized in human embryonic tissues.J Histochem Cytochem. 1997 Nov;45(11):1469-80. doi: 10.1177/002215549704501104. J Histochem Cytochem. 1997. PMID: 9358849
-
A unique tool to selectively detect the chondrogenic IIB form of human type II procollagen protein.Matrix Biol. 2014 Feb;34:80-8. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24055103
-
Type IIA procollagen: expression in developing chicken limb cartilage and human osteoarthritic articular cartilage.Dev Dyn. 2001 Apr;220(4):307-22. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.1109. Dev Dyn. 2001. PMID: 11307165
-
Modulation of collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage.Biorheology. 2004;41(3-4):535-42. Biorheology. 2004. PMID: 15299284 Review.
-
Expression of type II procollagens during development of the human intervertebral disc.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Nov;30(Pt 6):831-8. doi: 10.1042/bst0300831. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12440928 Review.
Cited by
-
Unusual Suspects: Bone and Cartilage ECM Proteins as Carcinoma Facilitators.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;15(3):791. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030791. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMPER, a novel endothelial cell precursor-derived protein, antagonizes bone morphogenetic protein signaling and endothelial cell differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(16):5664-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5664-5679.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12897139 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in type II procollagen isoform expression during chondrogenesis by disruption of an alternative 5' splice site within Col2a1 exon 2.Matrix Biol. 2014 Jun;36:51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24735995 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered cartilage using primary chondrocytes cultured in a porous cartilage-derived matrix.Regen Med. 2011 Jan;6(1):81-93. doi: 10.2217/rme.10.87. Regen Med. 2011. PMID: 21175289 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis in Mice Following Mechanical Injury to the Synovial Joint.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;7:45223. doi: 10.1038/srep45223. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28345597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bostrom MP, Lane JM, Berberian WS, Missri AA, Tomin E, Weiland A, Doty SB, Glaser D, Rosen VM. Immunolocalization and expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and 4 in fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 1995;13:357–367. - PubMed
-
- Brunet LJ, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Harland RM. Noggin, cartilage morphogenesis, and joint formation in the mammalian skeleton. Science. 1998;280:1455–1457. - PubMed
-
- Cheah KSE, Lau ET, Au PKC, Tam PPL. Expression of the mouse α1(II) collagen gene is not restricted to cartilage during development. Development. 1991;111:945–953. - PubMed
-
- Denker AE, Nicoll SB, Tuan RS. Formation of cartilage-like spheroids by micromass cultures of murine C3H10T1/2 cells upon treatment with transforming growth factor-beta 1. Differentiation. 1995;59:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Eikenberry EF, Childs B, Sheren SB, Parry DA, Craig AS, Brodsky B. Crystalline fibril structure of type II collagen in lamprey notochord sheath. J Mol Biol. 1984;176:261–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

