Effect of the microtubule polymerizing agent taxol on contraction, Ca2+ transient and L-type Ca2+ current in rat ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 10087341
- PMCID: PMC2269262
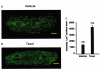
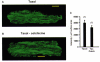
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0409v.x
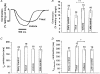
Effect of the microtubule polymerizing agent taxol on contraction, Ca2+ transient and L-type Ca2+ current in rat ventricular myocytes
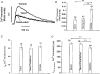
Abstract
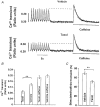
1. Microtubules form part of the cytoskeleton. Their role in adult ventricular myocytes is not well understood although microtubule proliferation has previously been linked with reduced contractile function. 2. We investigated the effect of the anti-tumour drug taxol, a known microtubule polymerizing agent, on Ca2+ handling in adult rat ventricular myocytes. 3. Treatment of cells with taxol caused proliferation of microtubules. 4. In taxol-treated cells there was a reduction in the amplitude of contraction, no significant effect on the amplitude of L-type Ca2+ current, but a significant reduction in the amplitude of the Ca2+ transient. 5. Caffeine was used to release Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). There was a significant reduction in the ratio of electrically stimulated : caffeine-induced Ca2+ transients in taxol-treated cells. This observation is consistent with the hypothesis that taxol reduces fractional SR Ca2+ release. 6. We suggest that the negative inotropic effect of taxol may, at least in part, be the result of reduced release of Ca2+ from the SR. Microtubules may be important regulators of Ca2+ handling in the heart.
Figures


References
-
- Arnal I, Wade RH. How does taxol stabilize microtubules? Current Biology. 1995;5:900–908. - PubMed
-
- Bassani JW, Yuan WL, Bers DM. Fractional SR Ca release is regulated by trigger Ca and SR Ca content in cardiac myocytes. American Journal of Physiology. 1995;37:C1313–1319. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force. Kluwer Academic Press; 1991.
-
- Brette F, Hongo K, Haroon MM, White E. Rapid negative inotropic effect of deuterium oxide in isolated ferret papillary muscles and single rat ventricular myocytes. The Journal of Physiology. 1996;491.P:157. P. - PubMed
-
- Cannell MB, Berlin JR, Lederer WJ. Effect of membrane potential changes on the calcium transient in single rat cardiac muscle cells. Science. 1987;238:1419–1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

