Raft association of SNAP receptors acting in apical trafficking in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 10097106
- PMCID: PMC22363
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3734
Raft association of SNAP receptors acting in apical trafficking in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
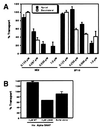
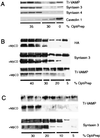
We have investigated the relationships between the apical sorting mechanism using lipid rafts and the soluble N-ethyl maleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) machinery, which is involved in membrane docking and fusion. We first confirmed that anti-alpha-SNAP antibodies inhibit the apical pathway in Madin- Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells; in addition, we report that a recombinant SNAP protein stimulates the apical transport whereas a SNAP mutant inhibits this transport step. Based on t-SNARE overexpression experiments and the effect of botulinum neurotoxin E, syntaxin 3 and SNAP-23 have been implicated in apical membrane trafficking. Here, we show in permeabilized MDCK cells that antisyntaxin 3 and anti-SNAP-23 antibodies lower surface delivery of an apical reporter protein. Moreover, using a similar approach, we show that tetanus toxin-insensitive, vesicle-associated membrane protein (TI-VAMP; also called VAMP7), a recently described apical v-SNARE, is involved. Furthermore, we show the presence of syntaxin 3 and TI-VAMP in isolated apical carriers. Polarized apical sorting has been postulated to be mediated by the clustering of apical proteins into dynamic sphingolipid-cholesterol rafts. We provide evidence that syntaxin 3 and TI-VAMP are raft-associated. These data support a raft-based mechanism for the sorting of not only apically destined cargo but also of SNAREs having functions in apical membrane-docking and fusion events.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel tetanus neurotoxin-insensitive vesicle-associated membrane protein in SNARE complexes of the apical plasma membrane of epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Jun;9(6):1437-48. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.6.1437. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9614185 Free PMC article.
-
The SNARE machinery is involved in apical plasma membrane trafficking in MDCK cells.J Cell Biol. 1998 Jun 29;141(7):1503-13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.7.1503. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9647644 Free PMC article.
-
The vesicle- and target-SNARE proteins that mediate Glut4 vesicle fusion are localized in detergent-insoluble lipid rafts present on distinct intracellular membranes.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 20;277(51):49750-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206936200. Epub 2002 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12376543
-
A new beat for the SNARE drum.Trends Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;8(6):215-8. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01272-0. Trends Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9695844 Review.
-
Syntaxin 16's Newly Deciphered Roles in Autophagy.Cells. 2019 Dec 17;8(12):1655. doi: 10.3390/cells8121655. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31861136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Syntaxin-3 regulates newcomer insulin granule exocytosis and compound fusion in pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2013 Feb;56(2):359-69. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2757-0. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23132338
-
Annexin A2 is involved in the formation of hepatitis C virus replication complex on the lipid raft.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(8):4139-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06327-11. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22301157 Free PMC article.
-
Transbilayer peptide sorting between raft and nonraft bilayers: comparisons of detergent extraction and confocal microscopy.Biophys J. 2005 Aug;89(2):1102-8. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.062380. Epub 2005 May 20. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15908585 Free PMC article.
-
Raft-partitioning of the ubiquitin ligases Cbl and Nedd4 upon IgE-triggered cell signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3180-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051003498. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11248052 Free PMC article.
-
v-SNARE cellubrevin is required for basolateral sorting of AP-1B-dependent cargo in polarized epithelial cells.J Cell Biol. 2007 May 7;177(3):477-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200610047. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17485489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodriguez-Boulan E, Powell S K. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:395–427. - PubMed
-
- Weimbs T, Low S-H, Chapin S J, Mostov K E. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7:393–399. - PubMed
-
- Scheiffele P, Simons K. In: Epithelial Morphogenesis in Development and Disease. Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C, editors. New York: Harwood; 1998. , in press.
-
- Simons K, Ikonen E. Nature (London) 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Brown D A, London E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;240:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

