A cluster of oppositely imprinted transcripts at the Gnas locus in the distal imprinting region of mouse chromosome 2
- PMID: 10097123
- PMCID: PMC22380
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3830
A cluster of oppositely imprinted transcripts at the Gnas locus in the distal imprinting region of mouse chromosome 2
Abstract
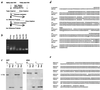
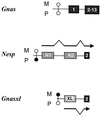
Imprinted genes tend to occur in clusters. We have identified a cluster in distal mouse chromosome (Chr) 2, known from early genetic studies to contain both maternally and paternally imprinted, but unspecified, genes. Subsequently, one was identified as Gnas, which encodes a G protein alpha subunit, and there is clinical and biochemical evidence that the human homologue GNAS1, mutated in patients with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, is also imprinted. We have used representational difference analysis, based on parent-of-origin methylation differences, to isolate candidate imprinted genes in distal Chr 2 and found two oppositely imprinted genes, Gnasxl and Nesp. Gnasxl determines a variant G protein alpha subunit associated with the trans-Golgi network and Nesp encodes a secreted protein of neuroendocrine tissues. Gnasxl is maternally methylated in genomic DNA and encodes a paternal-specific transcript, whereas Nesp is paternally methylated with maternal-specific expression. Their reciprocal imprinting may offer insight into the distal Chr 2 imprinting phenotypes. Remarkably, Gnasxl, Nesp, and Gnas are all part of the same transcription unit; transcripts for Gnasxl and Nesp are alternatively spliced onto exon 2 of Gnas. This demonstrates an imprinting mechanism in which two oppositely imprinted genes share the same downstream exons.
Figures
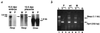

References
-
- Cattanach B M, Kirk M. Nature (London) 1985;315:496–498. - PubMed
-
- Beechey C V, Peters J. Mouse Genome. 1994;92:353–354.
-
- Dittrich B, Buiting K, Korn B, Rickard S, Buxton J, Saitoh S, Nicholls R D, Poutska A, Winterpacht A, Zabel B, et al. Nat Genet. 1996;14:163–170. - PubMed
-
- Paulsen M, Davies K R, Bowden L M, Villar A J, Franck O, Fuermann M, Dean W L, Moore T F, Rodrigues N, Davies K E, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1149–1159. - PubMed
-
- Williamson C M, Schofield J, Dutton E R, Seymour A, Beechey C V, Edwards Y H, Peters J. Genomics. 1996;36:280–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

