Characterization of inhibitory and stimulatory forms of the murine natural killer cell receptor 2B4
- PMID: 10097130
- PMCID: PMC22387
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3870
Characterization of inhibitory and stimulatory forms of the murine natural killer cell receptor 2B4
Abstract
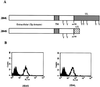
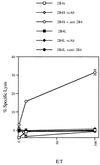
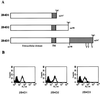
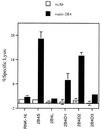
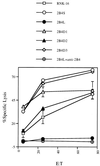
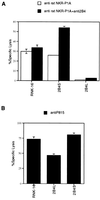
The receptor 2B4 belongs to the Ig superfamily and is found on the surface of all murine natural killer (NK) cells as well as T cells displaying non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity. Previous studies have suggested that 2B4 is an activating molecule because cross-linking of this receptor results in increased cytotoxicity and gamma-interferon secretion as well as granule exocytosis. However, it was recently shown that the gene for 2B4 encodes two different products that arise by alternative splicing. These gene products differ solely in their cytoplasmic domains. One form has a cytoplasmic tail of 150 amino acids (2B4L) and the other has a tail of 93 amino acids (2B4S). To determine the function of each receptor, cDNAs for 2B4S and 2B4L were transfected into the rat NK cell line RNK-16. Interestingly, the two forms of 2B4 had opposing functions. 2B4S was able to mediate redirected lysis of P815 tumor targets, suggesting that this form represents an activating receptor. However, 2B4L expression led to an inhibition of redirected lysis of P815 targets when the mAb 3.2.3 (specific for rat NKRP1) was used. In addition, 2B4L constitutively inhibits lysis of YAC-1 tumor targets. 2B4L is a tyrosine phosphoprotein, and removal of domains containing these residues abrogates its inhibitory function. Like other inhibitory receptors, 2B4L associates with the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Thus, 2B4L is an inhibitory receptor belonging to the Ig superfamily.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The murine NK receptor 2B4 (CD244) exhibits inhibitory function independent of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein expression.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 15;173(6):3953-61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.3953. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15356144
-
Cutting edge: the NK cell receptor 2B4 augments antigen-specific T cell cytotoxicity through CD48 ligation on neighboring T cells.J Immunol. 2003 May 15;170(10):4881-5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.4881. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12734329
-
Molecular characterization of the rat NK cell receptor 2B4.Mol Immunol. 2000 Aug-Sep;37(12-13):735-44. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(00)00103-6. Mol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11275258
-
Of mice and men: different functions of the murine and human 2B4 (CD244) receptor on NK cells.Immunol Lett. 2006 Jun 15;105(2):180-4. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16621032 Review.
-
Inhibition of natural killer cell activation signals by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (CD158).Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:223-33. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810119.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513144 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of natural killer receptor 2B4 bound to CD48 reveals basis for heterophilic recognition in signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family.Immunity. 2007 Oct;27(4):572-84. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.019. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17950006 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of CD244 Signaling in Immune Cells of the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 28;9:2809. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02809. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30546369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity of CD2 subfamily receptors in cyprinid fishes.Results Immunol. 2012 Feb 1;2:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.rinim.2012.01.003. eCollection 2012. Results Immunol. 2012. PMID: 24371564 Free PMC article.
-
Syngeneic leukemia models using lentiviral transgenics.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 18;12(2):193. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03477-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33602907 Free PMC article.
-
2B4 (CD244) signaling via chimeric receptors costimulates tumor-antigen specific proliferation and in vitro expansion of human T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Dec;58(12):1991-2001. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0704-9. Epub 2009 Apr 10. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 19360406 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

