Targeting Gbeta gamma signaling in arterial vascular smooth muscle proliferation: a novel strategy to limit restenosis
- PMID: 10097143
- PMCID: PMC22400
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3945
Targeting Gbeta gamma signaling in arterial vascular smooth muscle proliferation: a novel strategy to limit restenosis
Abstract
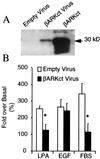
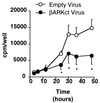
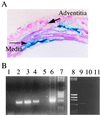
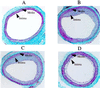
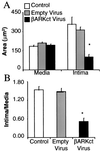
Restenosis continues to be a major problem limiting the effectiveness of revascularization procedures. To date, the roles of heterotrimeric G proteins in the triggering of pathological vascular smooth muscle (VSM) cell proliferation have not been elucidated. betagamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins (Gbetagamma) are known to activate mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases after stimulation of certain G protein-coupled receptors; however, their relevance in VSM mitogenesis in vitro or in vivo is not known. Using adenoviral-mediated transfer of a transgene encoding a peptide inhibitor of Gbetagamma signaling (betaARKct), we evaluated the role of Gbetagamma in MAP kinase activation and proliferation in response to several mitogens, including serum, in cultured rat VSM cells. Our results include the striking finding that serum-induced proliferation of VSM cells in vitro is mediated largely via Gbetagamma. Furthermore, we studied the effects of in vivo adenoviral-mediated betaARKct gene transfer on VSM intimal hyperplasia in a rat carotid artery restenosis model. Our in vivo results demonstrated that the presence of the betaARKct in injured rat carotid arteries significantly reduced VSM intimal hyperplasia by 70%. Thus, Gbetagamma plays a critical role in physiological VSM proliferation, and targeted Gbetagamma inhibition represents a novel approach for the treatment of pathological conditions such as restenosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenoviral-mediated inhibition of G beta gamma signaling limits the hyperplastic response in experimental vein grafts.Surgery. 1998 Aug;124(2):177-86. Surgery. 1998. PMID: 9706136
-
G protein signaling and vein graft intimal hyperplasia: reduction of intimal hyperplasia in vein grafts by a Gbetagamma inhibitor suggests a major role of G protein signaling in lesion development.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Aug;18(8):1275-80. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.8.1275. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9714134
-
Catheter-mediated delivery of adenoviral vectors expressing beta-adrenergic receptor kinase C-terminus inhibits intimal hyperplasia and luminal stenosis in rabbit iliac arteries.J Gene Med. 2004 Oct;6(10):1061-8. doi: 10.1002/jgm.592. J Gene Med. 2004. PMID: 15386742
-
G beta gamma-mediated signaling: new therapeutic target for proliferative vascular disease.IUBMB Life. 1999 Sep;48(3):257-61. doi: 10.1080/713803509. IUBMB Life. 1999. PMID: 10690635 Review.
-
In vivo adenoviral-mediated gene transfer of the beta ARKct to study the role of G beta gamma in arterial restenosis.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;237:181-92. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-430-1:181. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14501050 Review.
Cited by
-
Potentiation of TRAIL killing activity by multimerization through isoleucine zipper hexamerization motif.BMB Rep. 2016 May;49(5):282-7. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.5.245. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 26674343 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-associated protein stimulates alpha2beta1-dependent chemotaxis via Gi-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase and extracellular-regulated kinases.J Cell Biol. 1999 Oct 18;147(2):389-400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.2.389. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10525543 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-Adrenergic gene therapy for cardiovascular disease.Curr Control Trials Cardiovasc Med. 2000;1(3):131-134. doi: 10.1186/cvm-1-3-131. Curr Control Trials Cardiovasc Med. 2000. PMID: 11714426 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of E2F proteins in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and intimal hyperplasia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Aug 7;104(32):12988-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704754104. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17652516 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Role of G Protein βγ in Kv7-Dependent Relaxations of the Rat Vasculature.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Sep;38(9):2091-2102. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311360. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30002060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gruentzig A, Senning A, Siegenthaler W E. N Engl J Med. 1979;301:61–68. - PubMed
-
- DeFeyter P J, Serruys P W. In: Textbook of Interventional Cardiology. Topol E J, editor. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1994. pp. 274–291.
-
- Grines C L, Browne K F, Marco J, Rothbaum D, Stone G W, O’Keefe J, Overlie P, Donohue B, Chelliah N, Timmis G C. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:673–679. - PubMed
-
- McBride W, Lange R A, Hillis L D. N Engl J Med. 1988;318:1734–1737. - PubMed
-
- Holmes D R, Jr, Vlietstra R E, Smith H C, Vetrovec G W, Kent K M, Cowley M J, Faxon D P, Gruentzig A R, Kelsey S F, Detre K M. Am J Cardiol. 1984;53:77c–81c. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

